OPAL MCP Server: Setup & Installation Guide
A comprehensive guide to installing, configuring, and utilizing the OPAL MCP Server for advanced AI-driven data integration.

Introduction
Prior to the emergence of the Model Context Protocol (MCP), functionality provided by Virtuoso's OPAL add-on middleware layer was only accessible through a limited set of options. The introduction of MCP provides an open standards-based interface for loosely coupled interactions with the powerful capabilities offered by OPAL.
This functionality is packaged as a collection of tools that support a wide range of operations, including:
- Deductive interactions with relational tables and entity relationship graphs.
- Comprehensive query execution (read/write).
- Unified Data Space Administration (databases, knowledge graphs, filesystems).
- Virtual Database Management for remote data sources.
- Seamless interactions with a broad spectrum of LLMs.
- Access to specialized OPAL Assistants and OpenAPI-based web services.
This guide provides comprehensive instructions for setting up, configuring, and utilizing the OPAL MCP Server, unlocking a new era of AI-driven data integration.
Benefits
- Universal Accessibility: Exposes OPAL functionality to any application or LLM that understands the OpenAI specification.
- Enhanced Security: Implements robust, attribute-based access controls (ABAC) to ensure data privacy and security at a granular level.
- Simplified Integration: Offers a standardized API that simplifies the process of integrating OPAL's capabilities into new and existing workflows.
- Future-Proof: Aligns with modern development practices and the growing ecosystem of AI tools and services.
Capabilities
The OPAL MCP Server provides API access to a wide range of OPAL's core functionalities, including:
- Database Operations: Execute SQL queries, manage tables, and retrieve metadata.
- Graph Operations: Interact with graph data, manage named graphs, and perform complex graph-based queries.
- LLM Management: Register, bind, and manage Large Language Models for use within the OPAL ecosystem.
- Administrative Tasks: Perform database administration, manage user access, and configure system settings.
- AI-Powered Data Interaction: Leverage advanced features like
promptCompleteandchatPromptCompletefor sophisticated, context-aware data interactions.
Prerequisites
Important: Before proceeding with the OPAL MCP Server setup, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- MCP Experience: Administrative and operational familiarity with MCP setup and use, including experience with our MCP servers for ODBC, JDBC, pyODBC, ADO.NET, or SQLAlchemy.
- OPAL Installation: You must already have an installed and configured OPAL add-on for your Virtuoso instance before proceeding to configure MCP support via this MCP Server.
Setup and Installation
Setting up the OPAL MCP Server involves installing the necessary Virtuoso components and configuring them to work together. Follow these detailed steps:
Installation Steps
- Install Virtuoso: Download and install the latest on-premise Virtuoso
installer for your platform:
You can download the latest version from the official Virtuoso website.
- Install Required VAD Packages: Install the VAL and personal-assistant VADs via the Conductor or iSQL interfaces. These packages provide the core functionality needed for OPAL MCP Server operations.
- Access the Chat Interface: Navigate to your OPAL instance:
- Local:
https://localhost/chat - Remote:
https://{CNAME}/chat
- Local:
- Initial Login and LLM Setup: Log in with the default
dbausername. When prompted, enter your preferred Large Language Model (LLM) provider's API key to complete the initial setup.
Additional Components
Once your OPAL instance is up and running, you can optionally install additional
components using the Virtuoso Application Distribution (VAD) installer—available via the
Virtuoso Conductor UI or the isql command-line tool.
Important VAD Package Examples
1. Assistant-Metal UI
A user-friendly interface for interacting with OpenAI's Assistants API. This component enables you to create, test, deploy, and manage AI Agents/Assistants using natural language prompts written in Markdown.
2. Linked Data Cartridges
A powerful suite of data transformation tools that enhance data crawling across local and public HTTP networks (e.g., the Web). These transformations can be triggered by:
- SQL or SPARQL queries
- Briefcase folders
- Virtuoso's built-in web crawler
This package also includes a Meta Cartridge that integrates LLM-based batch processing. For example, given the URL of an HTML document, the system can:
- Trigger a batch task (executed asynchronously by the selected LLM)
- Transform content into RDF-based Knowledge Graphs
- Upload the resulting Knowledge Graph into Virtuoso's native RDF store for Entity Relationship Graphs
These VAD packages significantly expand your OPAL instance's capabilities—enabling advanced data workflows driven by entity relationship types defined in ontologies and enhanced through loosely coupled LLM integrations.
Supported LLMs
Any LLM that provides an API compatible with the OpenAPI specification can be registered and used with the OPAL. This includes popular models from providers like:
- OpenAI — GPT family
- Google — Gemini and Gemma families
- Anthropic — Claude family
- Microsoft — GPT, Grok, and Phi families
- Perplexity — Sonar
- xAI — Grok family
- Mistral — Mistral family
- Alibaba — Qwen family
- DeepSeek — DeepSeek R family
- Meta — Llama family (via Groq or Cerebras)
Note: Other hosted or local LLMs that support OpenAI's Tools API for external function call integration are also supported.
Attribute-based Access Controls (ABAC)
At this point, you need to secure your OPAL and LLM integrated environment by using fine-grained access controls to determine who is allowed to log into your assistant and under what constraints (restrictions). You achieve this by executing the following commands (using the Conductor or ISQL command-line interfaces) that set up these powerful access controls.
Fine-grained access controls use entity relationship graphs comprising relationships, authorizations, restrictions, groups, and agents (people or bots) that are named unambiguously using standardized identifiers (e.g., Internationalized Resource Identifiers [IRIs]) with terms from ontologies such as:
- W3C's Access Control Ontology
- OpenLink Software's Access Control Ontology
- OpenLink Software's Restrictions Ontology
- Friend Of A Friend [FOAF] Ontology
Create Login Authorization for OPAL via /chat endpoint
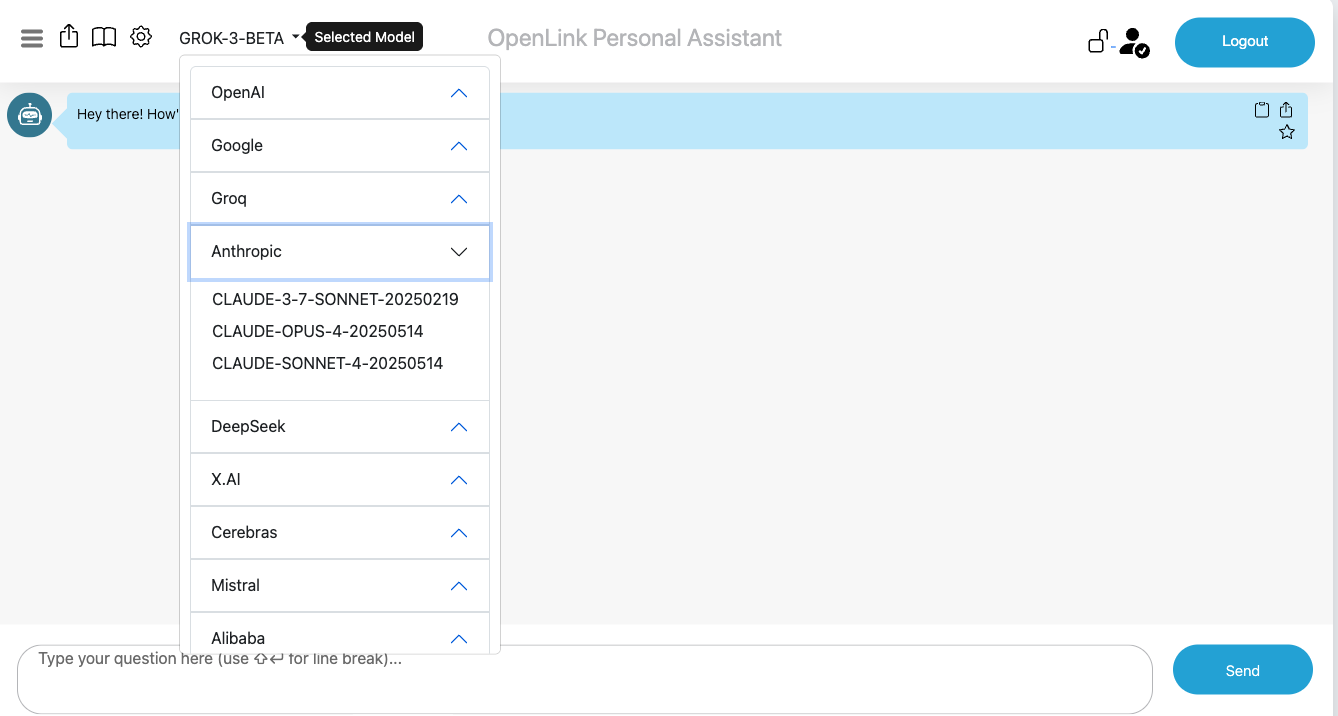
OPAL is denoted by the system identifier urn:oai:chat, which makes it possible
to construct an authorization for logins that belong to a designated group or list of users.
In this case, we simply want to set the authorization scope to the DBA user denoted by the
identifier http://localhost/dataspace/person/dba#this as follows:
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
PREFIX oplres: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/restrictions#>
WITH <urn:virtuoso:val:default:rules>
DELETE {
<#rulePublicChat> ?p ?o .
} WHERE {
<#rulePublicChat> a acl:Authorization ; ?p ?o .
}
INSERT {
<#rulePublicChat> a acl:Authorization ;
foaf:maker <#dba> ;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:Read, oplacl:Write ;
acl:accessTo <urn:oai:chat> ;
acl:agent <http://localhost/dataspace/person/dba#this> ;
oplacl:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm ;
oplacl:hasScope oplacl:Query .
} ;Create Login Authorization for OPAL via /assist-metal endpoint
If you want to extend the login access to OPAL's Assistants functionality via its
/assist-metal endpoint, then execute the following to create a restriction on
urn:oai:assistants (which is how this functionality realm is denoted):
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX oplres: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/restrictions#>
WITH <urn:virtuoso:val:default:rules>
INSERT
{
<#assistantsAdmin> a acl:Authorization ;
foaf:maker <#dba> ;
oplacl:hasAccessMode oplacl:Read, oplacl:Write ;
acl:accessTo <urn:oai:assistants> ;
acl:agent <http://localhost/dataspace/person/dba#this> ;
oplacl:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm ;
oplacl:hasScope oplacl:Query .
} ;System-wide LLM API Key Registration
Rather than repetitively entering LLM API Keys when you log in, it might be preferred to have those keys registered system-wide. To achieve this goal, you need to create a restriction for successfully logged-in users by executing the following:
PREFIX acl: <http://www.w3.org/ns/auth/acl#>
PREFIX oplacl: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/acl#>
PREFIX foaf: <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/>
PREFIX oplres: <http://www.openlinksw.com/ontology/restrictions#>
WITH <urn:virtuoso:val:default:restrictions>
DELETE {
?s ?p ?o .
}
WHERE {
?s a oplres:Restriction ;
oplres:hasRestrictedResource <urn:oai:chat> ; ?p ?o .
FILTER(?s = <#restrictionAuthChatKey>)
}
INSERT {
<#restrictionAuthChatKey> a oplres:Restriction ;
foaf:maker <#dba> ;
rdfs:label "Allow Api Key" ;
oplres:hasRestrictedResource <urn:oai:chat> ;
oplres:hasRestrictedParameter <urn:oai:chat:enable-api-keys> ;
oplres:hasRealm oplacl:DefaultRealm ;
oplres:hasAgent <http://localhost/dataspace/person/dba#this> ; ### list of NetIds to have access for system key
oplres:hasRestrictedValue "true"^^xsd:boolean .
} ;Large Language Models Registration & Use
With your OPAL instance successfully initialized, you can now bind it to one or more LLMs from the supported list. You achieve this via the following commands executed via the Conductor or iSQL interfaces.
Listing Bound LLMs
Command Syntax:
OAI.DBA.FILL_CHAT_MODELS('{Api Key}', '{llm-vendor-tag}');Where llm-vendor-tags are: alibaba, claude, deepseek, gemini, groq, mistral, openai, xai.
Usage Examples:
OAI.DBA.FILL_CHAT_MODELS('sk-xxxx', 'openai');
OAI.DBA.FILL_CHAT_MODELS('sk-ant-xxx', 'claude');Google DeepMind's Gemini does not currently offer an API for LLM listing, so you use:
OAI.DBA.REGISTER_CHAT_MODEL('{llm-vendor-tag}','{llm-name}');Usage Example:
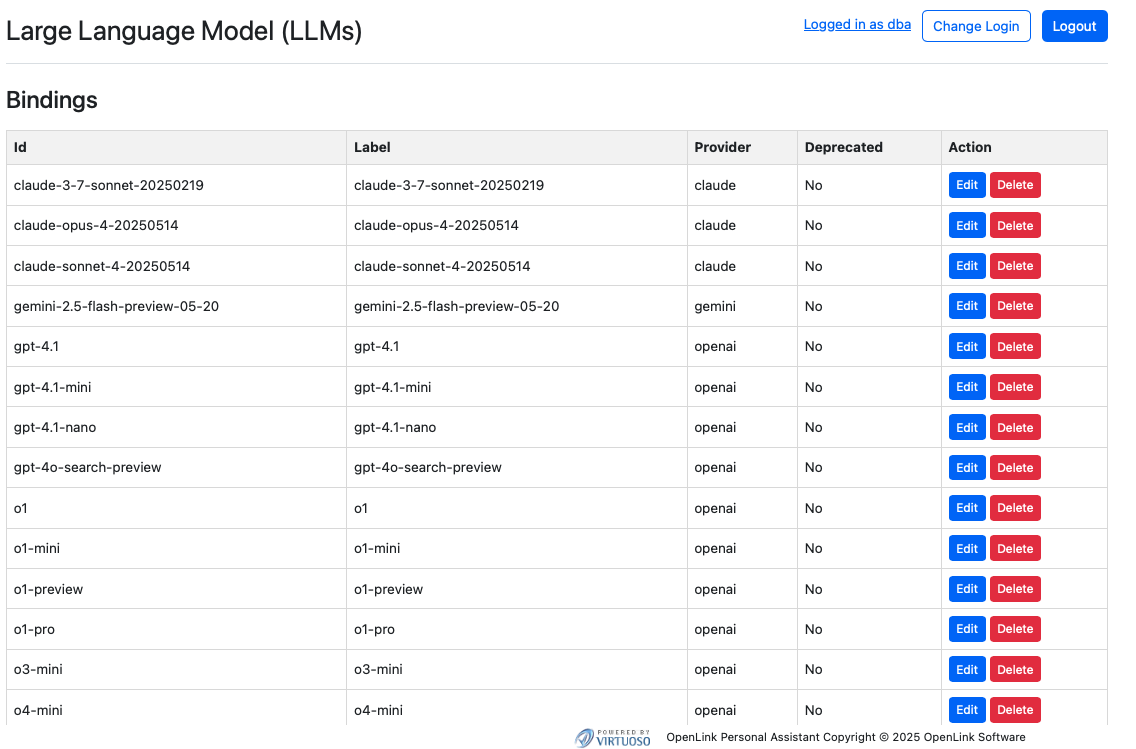
OAI.DBA.REGISTER_CHAT_MODEL('gemini','gemini-2.5-flash-preview-05-20');You can view the effects of this command via the Bound LLMs endpoint at:
https://{CNAME}/chat/admin/models.vsp
System-Wide LLM API Key Registration
To negate the need to present API Keys for bound LLMs at login time, you can register the API Keys for your chosen LLMs via the following command using the Conductor or ISQL command line interfaces:
Command Syntax:
OAI.DBA.SET_PROVIDER_KEY( '{llm-vendor-tag}', 'api-key')Usage Examples:
OAI.DBA.SET_PROVIDER_KEY('openai','sk-svcacct-xxx');
OAI.DBA.SET_PROVIDER_KEY('claude','sk-ant-api03-xxx');
OAI.DBA.SET_PROVIDER_KEY('gemini','AIxxxx');Application Programming Interface (API) Access
Your OPAL instance is also API-accessible, providing functionality for issuing and revoking credentials in the form of:
- Dynamically negotiated OAuth access tokens
- Issued OAuth Credentials and Bearer Tokens
You obtain credentials using the https://{CNAME}/oauth/applications.vsp
endpoint, which presents you with the following:
Client Applications Landing Page
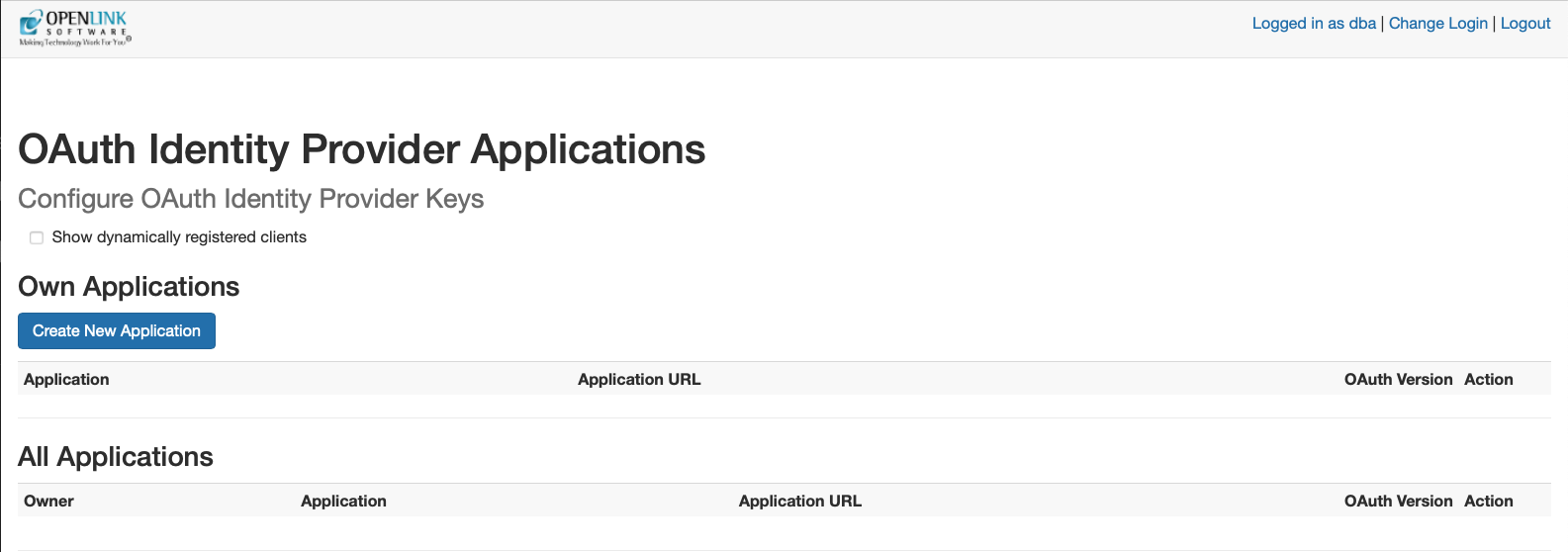
Credentials Issue Pages
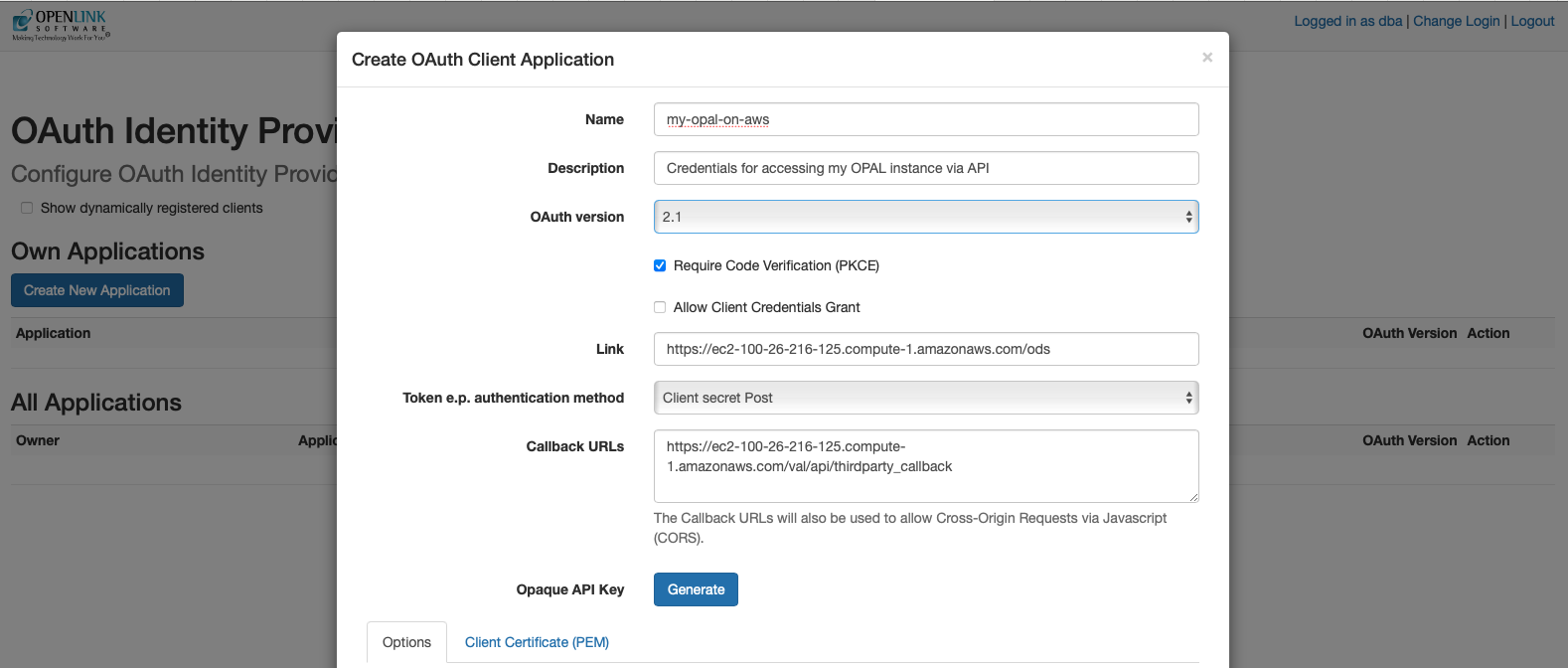
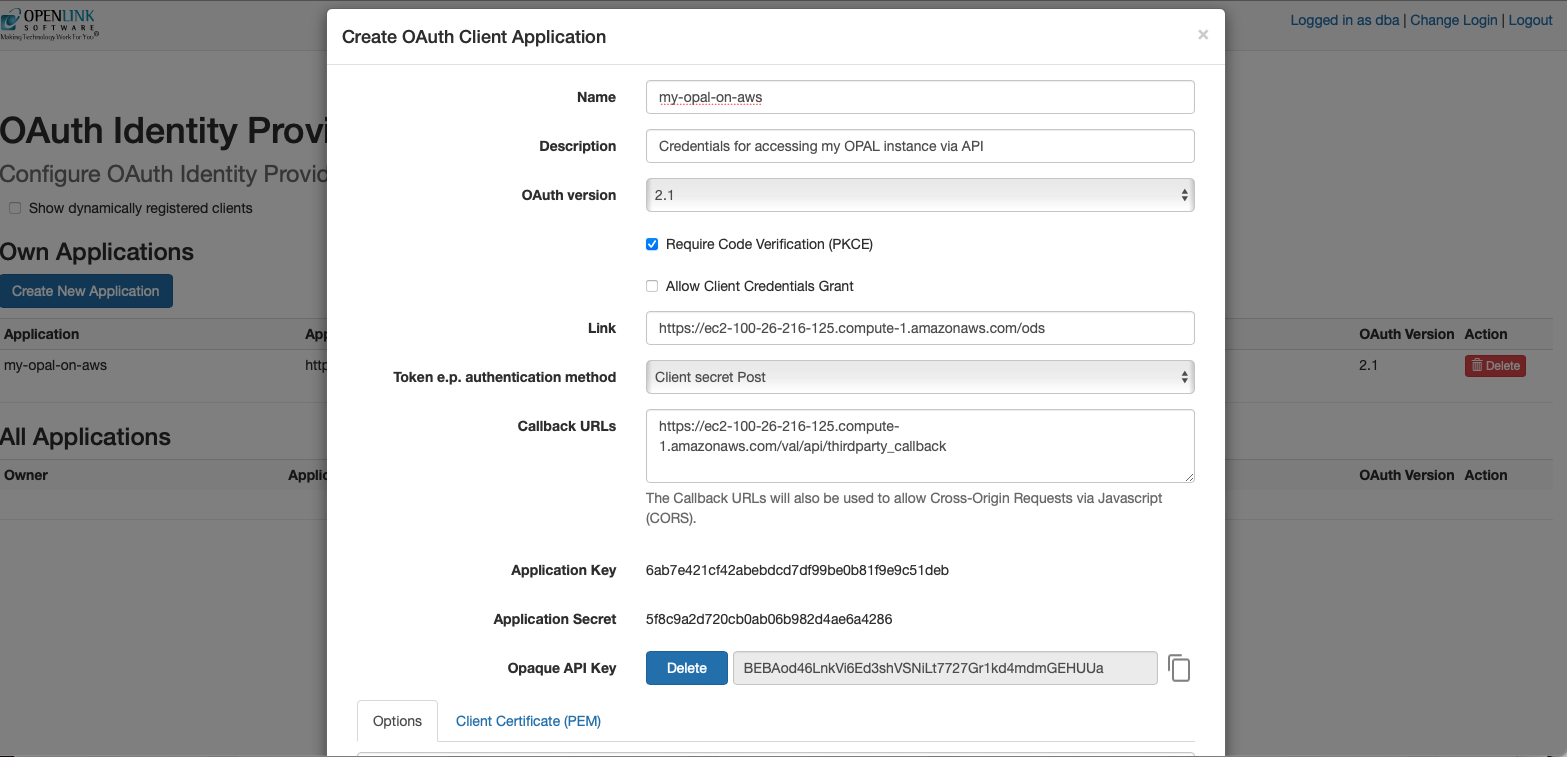
Once your credentials have been generated and copied to a safe location, you are ready for API-based interaction with your instance using protocols such as the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and the Agent-2-Agent (A2A) Protocol.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Usage
OPAL includes built-in support for the MCP protocol as both a client and a server, supporting the Server Sent Events (SSE) and Streamable HTTP transport options. This protocol offers direct access to AI Agents/Assistants created using natural language via Markdown with native stored procedures or external OpenAPI-accessible web services as the underlying tooling for executing operations.
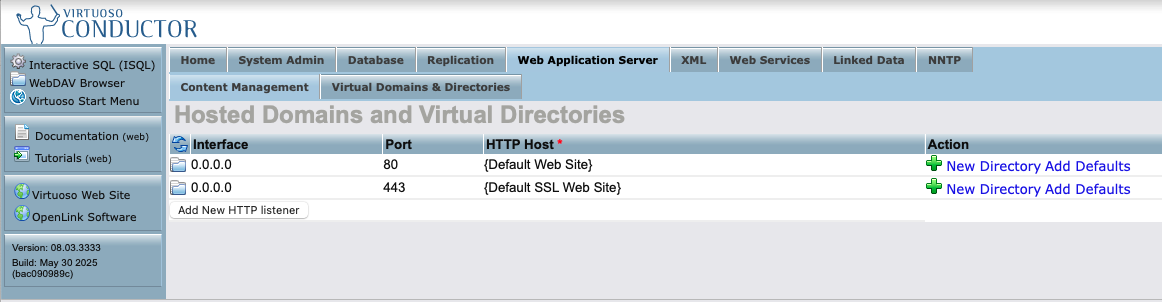
To enable use of this protocol, you will need to set up CORS access for your MCP client regarding the following virtual directories via the Conductor UI:
/.well-known/OAuth2
Here's a screenshot sequence depicting how this task is performed for the
/OAuth2 virtual directory.
HTTP Server's Virtual Domains
Virtual Directories Listing for the HTTPS Virtual Domain
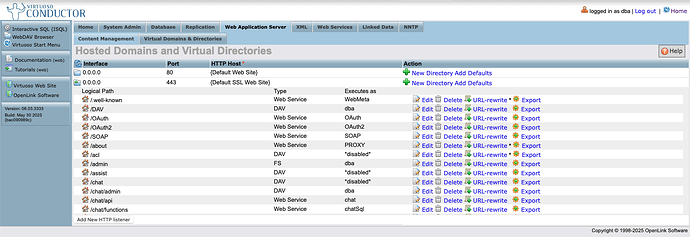
CORS Accepted Client Origins Listing
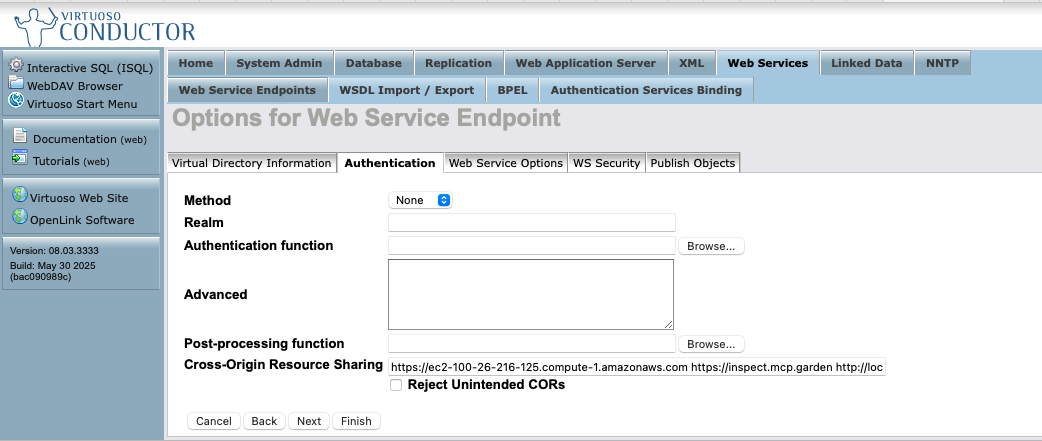
Note: Click "Finish" and then "Save Changes" for the CORS settings to take effect.
MCP Server Endpoints
The following endpoints are automatically generated for your OPAL instance:
https://{CNAME}/chat/mcp/messages– for the Streamable HTTP transporthttps://{CNAME}/chat/mcp/sse– for the Server Sent Events transport
Claude Desktop Configuration
Here's the JSON-based MCP Server configuration template for Claude Desktop:
{
"mcpServers": {
"{Your-Designated-MCP-Server-Name-For-SSE}": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"https://{CNAME}/chat/mcp/sse"
]
},
"{Your-Designated-MCP-Server-Name-For-Streamable-HTTP}": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"https://{CNAME}/chat/mcp/messages"
]
}
}
}Claude Desktop Screencast Demo
MCP Inspector
By default, your AWS hosted OPAL instance uses an HTTPS configuration based on a self-signed certificate generated by Virtuoso. As a result, you need to set the following environment variable before starting your MCP inspector sessions:
export NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED=0Naturally, if you reconfigure your instance to use your CA-signed certificate or leverage Virtuoso's native support for the ACME protocol, you can work around this MCP inspector interaction limitation.
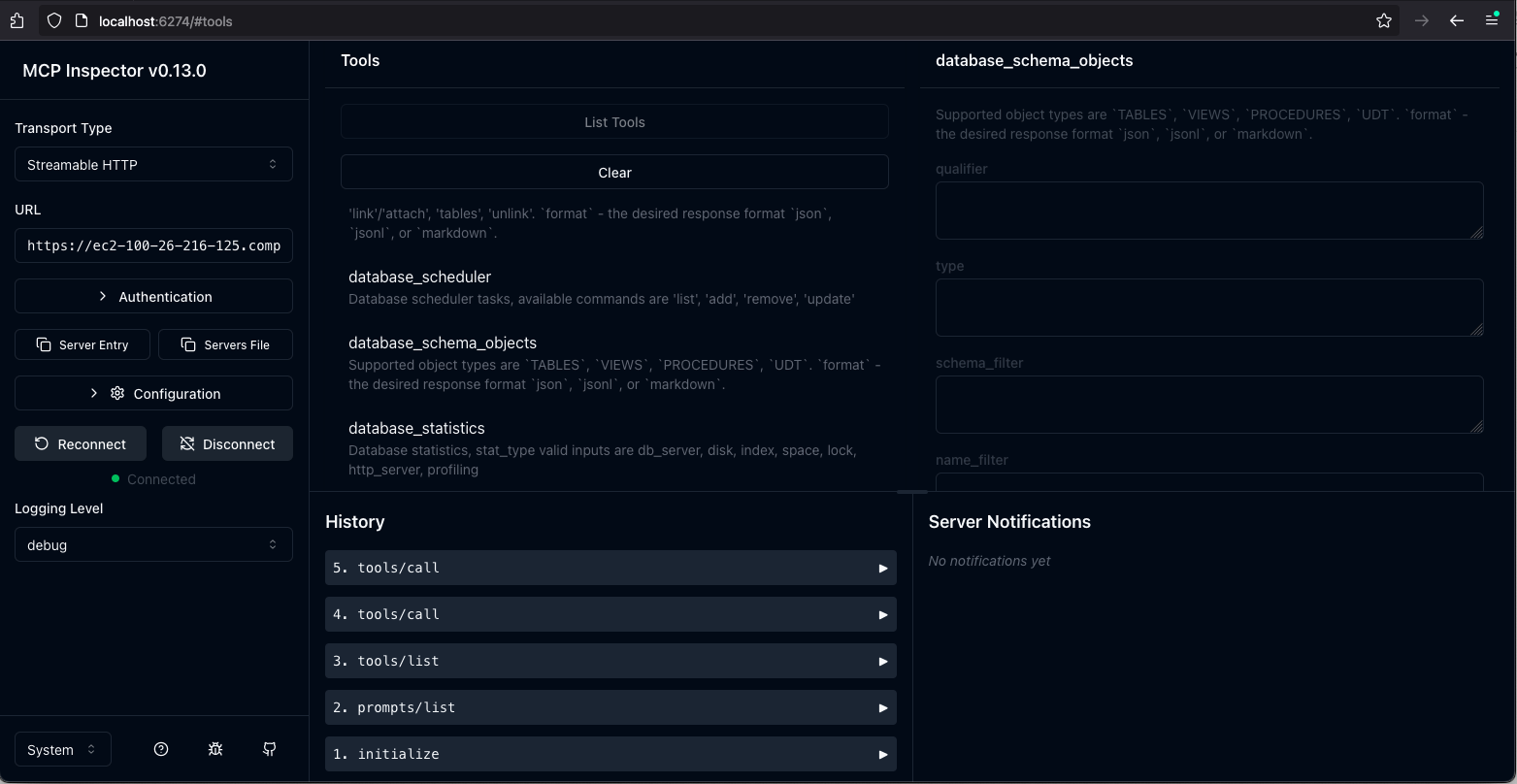
Your OPAL instance as an MCP Client
As an MCP client, OPAL is able to bind to tools published by any MCP Server that provides a Streamable HTTP endpoint. For example, our public endpoints:
https://demo.openlinksw.com/chat/mcp/messageshttps://linkeddata.uriburner.com/chat/mcp/messages
You can test this capability using our public MCP endpoints via the following steps:
- Obtain Access Credentials in the form of an API Key
- Go to the following endpoint for your AWS instance:
https://{CNAME}/chat/admin/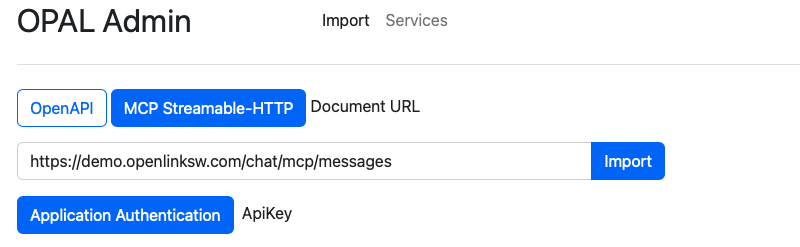
- Click on the "Application Authentication" button, which presents an
authentication dialog from which you can select the "API Key" tab for registering the
API Key obtained in step 1
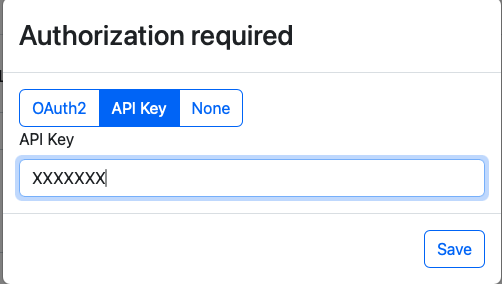
- Authenticate, and if successful you will be presented with a list of
tools from the remote MCP server.
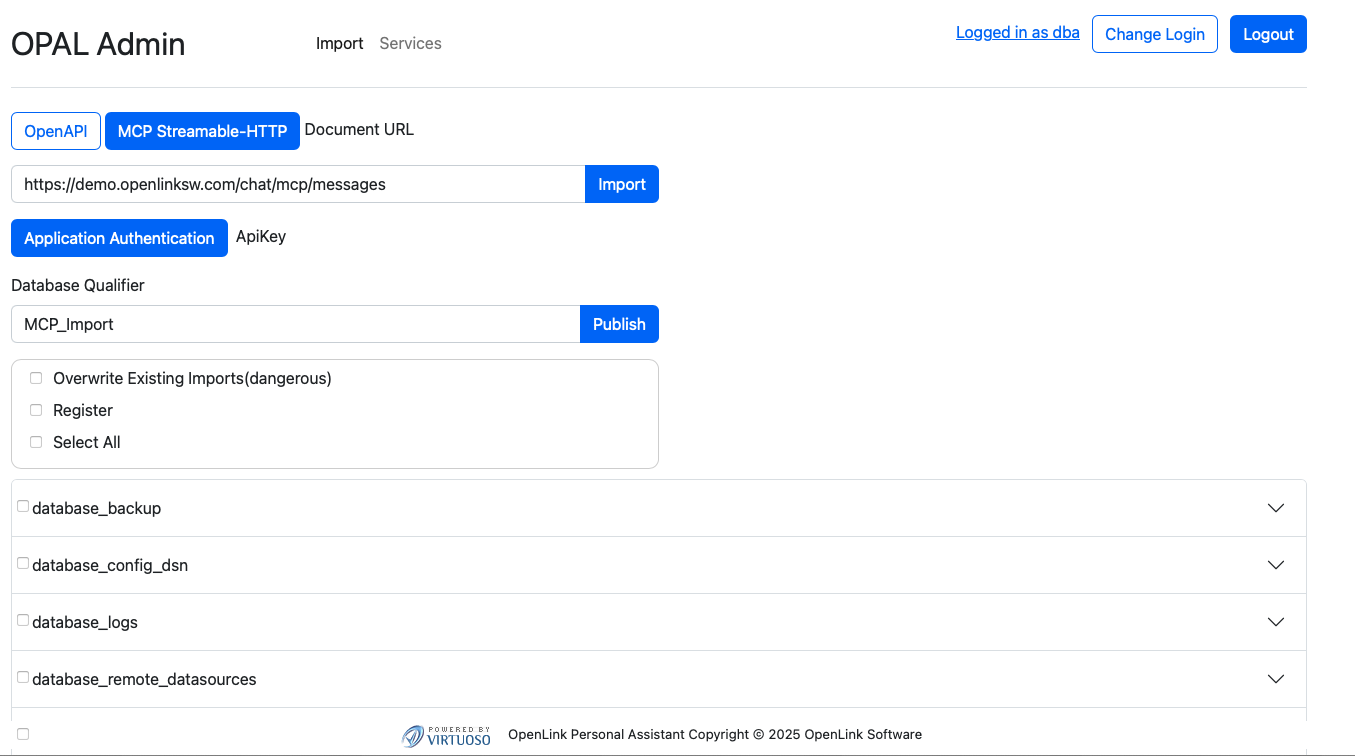
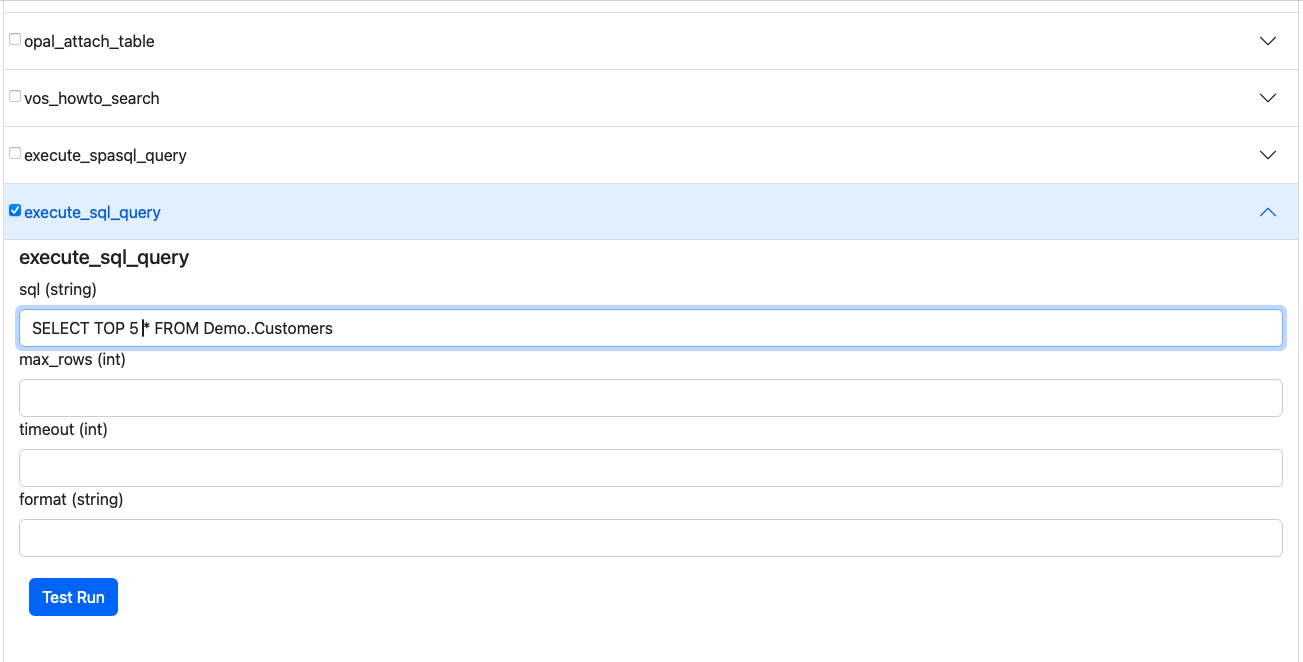
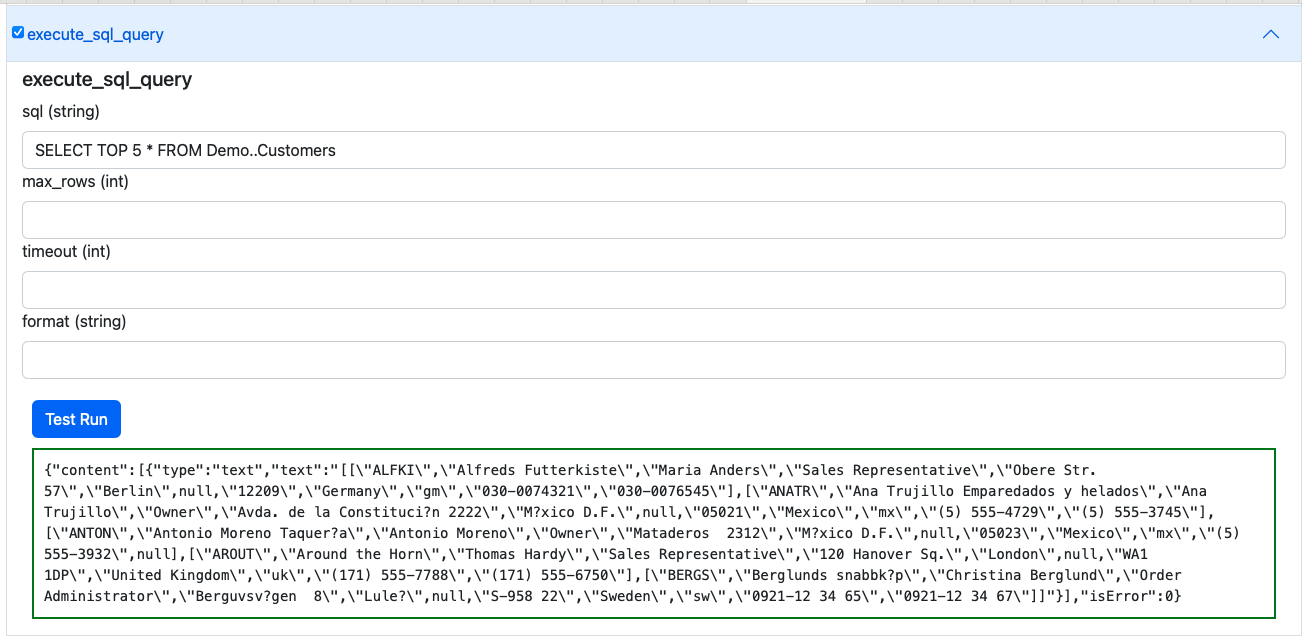
- Select a Tool of interest from the MCP Server e.g., execute_sql_query
and then expand by clicking on the expand control to interact with the SQL capture
interface.
Other MCP Interaction Options
The following MCP Servers also offer bridge-based access to your OPAL instance, courtesy of the stdio transport leveraging data access protocols:
- OpenLink Generic MCP Server for ODBC (for JavaScript/TypeScript runtimes like Node.js)
- OpenLink Generic MCP Server for JDBC (for Java runtimes)
- OpenLink Generic MCP Server for pyODBC (for Python runtimes)
- OpenLink Virtuoso MCP Server for ADO.NET (for .NET runtimes)
Agent-2-Agent (A2A) Protocol Usage
A2A support provides access to AI Agents/Assistants created and deployed using your OPAL
instance. It also enables their use in the construction of sophisticated Agentic workflows
that route requests across these Agents. Agents are discoverable to all A2A client
applications and services via an automatically generated JSON-based Agent Card situated at:
https://{CNAME}/.well-known/agent.json.
This file comprises the description of an Agent (named "OPAL Agent") that's equipped with a collection of skills, each of which is associated with an Agent/Assistant comprising MCP-accessible or directly-accessible tools that are mapped to operations based on native stored procedures, OpenAPI-compliant web services, or tools published by other MCP servers.
Default Agent Card for OPAL instances
{
"name": "OPAL Agent",
"description": "OpenLink AI Layer",
"url": "https://ec2-100-26-216-125.compute-1.amazonaws.com/chat/api/a2a",
"version": "1.0.0",
"provider": {
"organization": "OpenLink Software",
"url": "https://www.openlinksw.com"
},
"authentication": {
"schemes": [
"OAuth2"
],
"credentials": "{\"authorizationUrl\":\"https://ec2-100-26-216-125.compute-1.amazonaws.com/OAuth2/authorize\",\"tokenUrl\":\"https://ec2-100-26-216-125.compute-1.amazonaws.com/OAuth2/token\",\"scopes\":[\"openid\",\"profile\"]}"
},
"capabilities": {
"streaming": true,
"pushNotifications": false,
"stateTransitionHistory": false
},
"defaultInputModes": [
"text",
"text/plain"
],
"defaultOutputModes": [
"text",
"text/plain"
],
"skills": [
{
"id": "system-data-twingler-config",
"name": "OpenLink Data Twingler v2.0.4",
"description": "OpenLink Data Twingler v2.0.4",
"tags": []
},
{
"id": "system-database-admin-config",
"name": "Virtuoso DB Admin Assistant v1.0.0",
"description": "Virtuoso DB Admin Assistant v1.0.0",
"tags": []
},
{
"id": "system-uda-support-assistant-config",
"name": "OpenLink Support Agent for ODBC and JDBC v1.0.22",
"description": "OpenLink Support Agent for ODBC and JDBC v1.0.22",
"tags": []
},
{
"id": "system-val-admin-config",
"name": "Virtuoso Authentication Layer (VAL) Assistant v1.0.0",
"description": "Virtuoso Authentication Layer (VAL) Assistant v1.0.0",
"tags": []
},
{
"id": "system-virtuoso-support-assistant-config",
"name": "Virtuoso Support Agent v1.1.45",
"description": "Virtuoso Support Agent v1.1.45",
"tags": []
}
]
}A2A Usage Example
Here's a simple example from the A2A Samples Collection from OpenLink's fork of Google's A2A repository on Github.
Instructions take the form:
User: [Using]
Where [] is optional and <> is mandatory.
Here's output captured from a session involving an A2A client and an OPAL Agent:
npx tsx src/cli.ts https://{CNAME} {OPAL-INSTANCE-API-KEY}
ENDPOINT {CNAME}/chat/api/a2a
✓ Agent Card Found:
Name: OPAL Agent
Description: OpenLink AI Layer
Version: 1.0.0
Streaming: Supported
No active task or context initially. Use '/new' to start a fresh session or send a message.
Enter messages, or use '/new' to start a new session. '/exit' to quit.
OPAL Agent > You:
OPAL Agent > You: /new
✨ Starting new session. Task and Context IDs are cleared.
OPAL Agent > You: Using the Data Twingler, execute: SPARQL SELECT ?s ?name WHERE { SERVICE <https://dbpedia.org/sparql> {SELECT DISTINCT * WHERE {?s a foaf:Person; foaf:name ?name.} LIMIT 5}}
Sending message...
OPAL Agent [10:45:58 AM]: ℹ️ Task Stream Event: ID: 7557962efbbb266b16198632ca925237, Context: 5bf8bc79a99845b8bc4900452d2d31fb, Status: submitted
Task ID updated from N/A to 7557962efbbb266b16198632ca925237
Context ID updated from N/A to 5bf8bc79a99845b8bc4900452d2d31fb
OPAL Agent [10:46:09 AM]: 📄 Artifact Received: (unnamed) (ID: a0c76a0c-4152-11f0-a842-9a642c1c243f, Task: 7557962efbbb266b16198632ca925237, Context: 5bf8bc79a99845b8bc4900452d2d31fb)
Part 1: 📝 Text: Here are the results of your SPARQL query:
| s | name |
|-------------------------------------------------|--------------------|
| [CaMia Hopson](http://dbpedia.org/resource/CaMia_Hopson) | CaMia Jackson |
| [Cab Calloway](http://dbpedia.org/resource/Cab_Calloway) | Cab Calloway |
| [Cab Kaye](http://dbpedia.org/resource/Cab_Kaye) | Cab Kaye |
| [Cabbrini Foncette](http://dbpedia.org/resource/Cabbrini_Foncette) | Cabbrini Foncette |
| [Cabell Breckinridge](http://dbpedia.org/resource/Cabell_Breckinridge) | Cabell Breckinridge |
These are distinct individuals identified as persons with their names retrieved from the DBpedia SPARQL endpoint.
OPAL Agent [10:46:09 AM]: ✅ Status: completed (Task: 7557962efbbb266b16198632ca925237, Context: 5bf8bc79a99845b8bc4900452d2d31fb) [FINAL]
Task 7557962efbbb266b16198632ca925237 is final. Clearing current task ID.
--- End of response stream for this input ---FAQ
What is the difference between OPAL and the OPAL MCP Server?
OPAL is the underlying middleware layer that provides the core data integration functionality. The OPAL MCP Server is a component that exposes this functionality through a modern, secure, and open API based on the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Do I need a separate license for the OPAL MCP Server?
The OPAL MCP Server is included as part of the standard Virtuoso licensing. No separate license is required.
Can I use my own custom access control policies?
Yes, the ABAC model is highly flexible and allows you to create your own custom policies to meet your specific security requirements.
Glossary
- MCP (Model Context Protocol)
- An open protocol for securely connecting Large Language Models (LLMs) with application servers and data sources.
- OPAL (OpenLink AI Layer)
- A middleware layer that provides powerful data integration and virtualization capabilities.
- ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control)
- A flexible and granular access control model that defines policies based on attributes of the user, data, and context.
- VAD (Virtuoso Application Distribution)
- A package format for distributing and installing applications and modules within the Virtuoso platform.
