Why Use an ODBC-to-JDBC Bridge?
This guide addresses a common and critical scenario where ODBC-compliant applications (including BI tools, spreadsheets, and custom applications) need to access data sources that offer only a JDBC driver — such as modern big data platforms, NoSQL databases, and various Java-based systems. The OpenLink ODBC-to-JDBC Bridge seamlessly translates between these two standards, unlocking access that would otherwise be impossible. The Enterprise Edition provides this core functionality with several powerful advantages:
Fine-Grained Access Control
Powerful attribute-based access controls (ABAC) as ODBC session-level enforcers of data access policies, aligned with governance requirements and compliance standards.
Enhanced Data Security
Comprehensive protection mechanisms addressing data security and privacy challenges, ensuring sensitive information is protected at the session level.
Deployment Flexibility
Flexible topology options essential for managing large-scale ODBC-based client applications and services in enterprise environments.
Product Overview
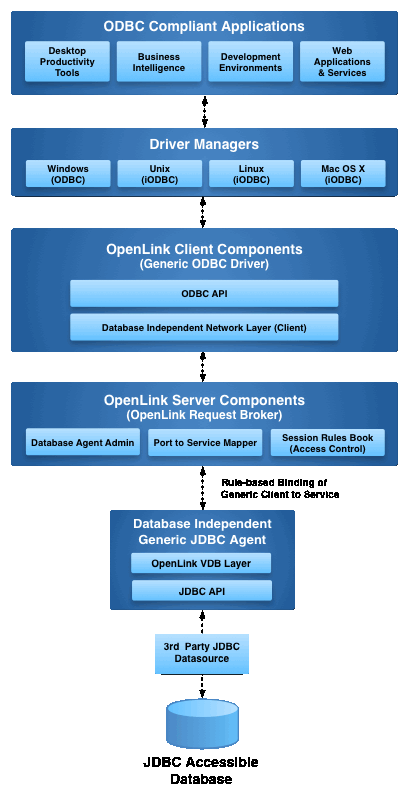
Enterprise Architecture
The OpenLink ODBC to JDBC Bridge implements a multi-tier architecture that enables seamless interoperability between ODBC-compliant clients and JDBC data sources. This client-side, multi-tier driver installs on a Windows machine and acts as a client to a remote database server, intelligently translating ODBC calls into JDBC calls.
Installation Guide
Follow these four steps to install the OpenLink ODBC to JDBC Bridge Connector on your Windows system.
Download the Installer Archive
Visit the OpenLink ODBC Enterprise Edition Driver Download Page or use curl to
download the required MSI installer archives for the driver components. You will need three MSI
files: waajzzzz.msi, wabrzzzz.msi, and wao3zzzz.msi.
Pre-Installation Configuration
Ensure a 64-bit JVM is installed, the target JDBC driver is available, and connection details like class name and URL are known. The JDBC driver's .jar file must be in the CLASSPATH, and the jvm.dll file must be located in the PATH environment variable.
Installation
Log onto the target machine and run each downloaded MSI installer to install the client and server components of the Enterprise Multi-Tier ODBC-JDBC Bridge. Take care to enter correct information when prompted, such as ports and passwords, and note them for future use.
Post-Installation Configuration
Set Java CLASSPATH and PATH variables in the OpenLink Rule Book (oplrqb.ini) if not
set system-wide, and place license files (oplrqb.lic and jdbc.lic) in
the installation's bin directory.
Java Environment Setup & JDBC Testing
Proper Java configuration is critical for the ODBC-JDBC Bridge to function correctly. This section covers environment setup and includes a complete JDBC testing utility to verify your configuration before proceeding to ODBC setup.
Locate JDBC Driver JAR Files
Determine the location of the JAR files for each JDBC driver you plan to use. Ideally, place all JDBC driver JARs in a common directory for easier management.
Set CLASSPATH Environment Variable
Ensure the CLASSPATH operating system environment variable includes entries for each JDBC driver JAR file location.
- Press
Win + Xand select System, then click Advanced system settings. - Click Environment Variables.
- Under System variables, click New. Set Variable name to
CLASSPATHand Variable value to your driver directory (e.g.,C:\Program Files\JDBC\*).
Create and Run UniversalJDBCTest
Save the following Java source code as UniversalJDBCTest.java. This utility
discovers installed JDBC drivers and tests their connectivity interactively.
// UniversalJDBCTest.java source code here...
// (Code from previous example)
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.Console;
// ... full code
- Compile:
javac UniversalJDBCTest.java - Run:
java -cp ".;C:\Program Files\JDBC\*" UniversalJDBCTest - Follow the interactive prompts to test your JDBC drivers.
ODBC DSN Configuration
Once installed and your Java environment is verified, configure your Data Source Names (DSNs) and test the connection using these steps.
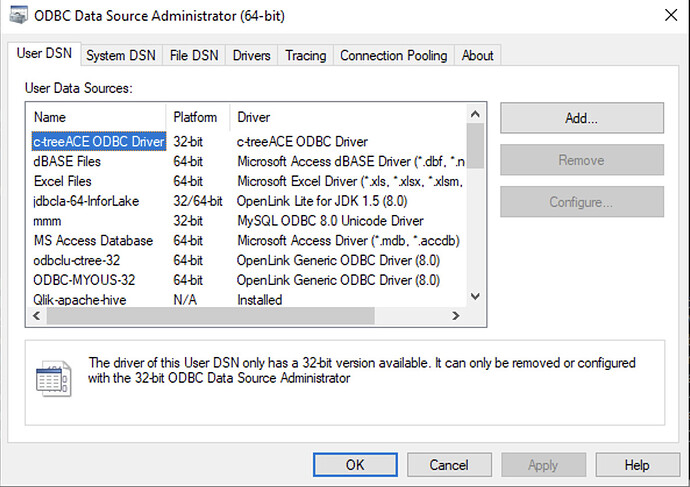
Open ODBC Administrator
Launch the ODBC Data Source Administrator program (32-bit or 64-bit as appropriate).
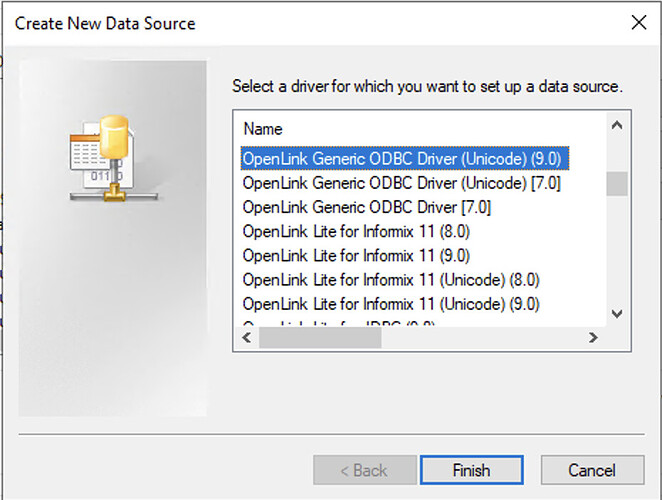
Add New Driver
Click the Add button and select the OpenLink Generic ODBC Driver (Unicode)(9.0) from the list.
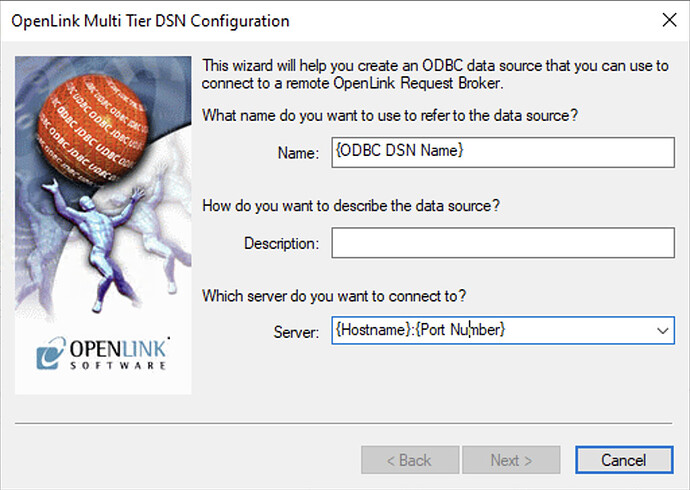
Configure Connection Details
Enter the ODBC DSN name and connection details (hostname and port number). Default is localhost:5000 for local connections.
Specify JDBC Connection Parameters
Select the Domain Jdbc 1.8, enter the JDBC Driver Name, JDBC Connect String URL, and login credentials. Check Connect now to verify... and click Next.
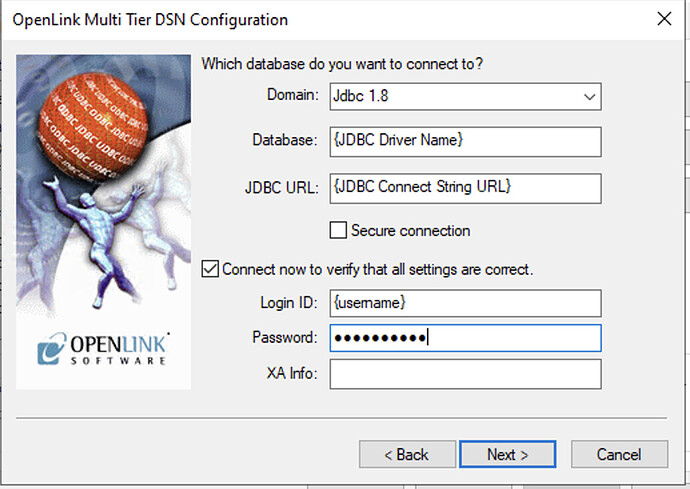
Test and Finalize
Review the optional settings, then use the Test Data Source button on the final screen to verify the connection. A success message confirms proper configuration.
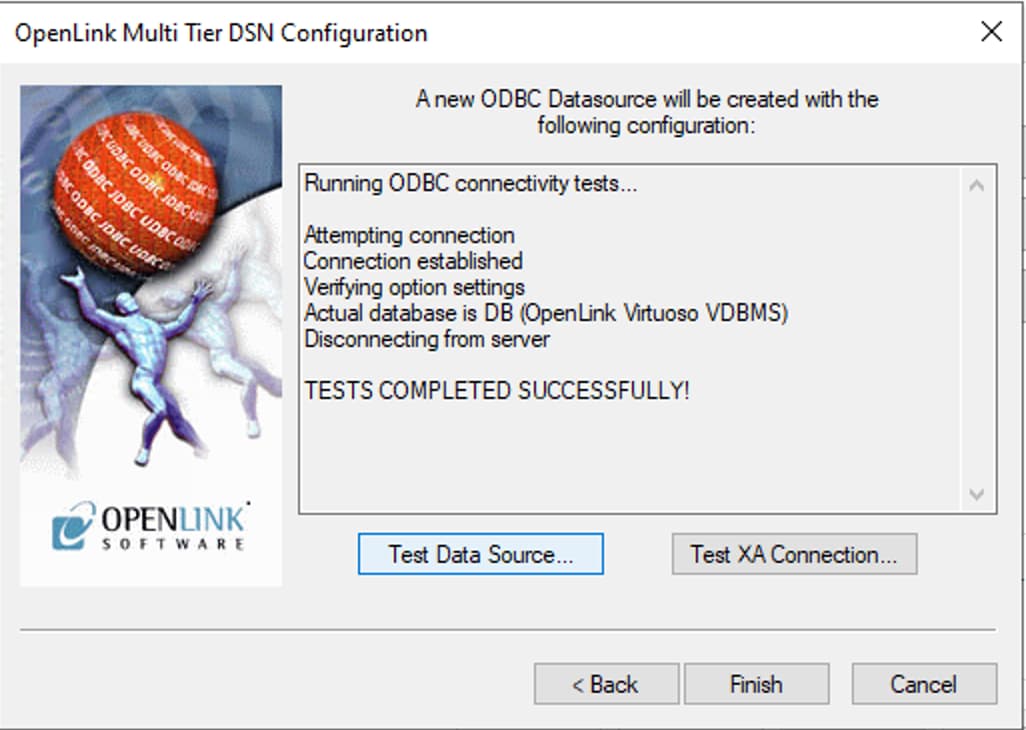
Testing & Troubleshooting
Using the C++ Demo Application
The C++ Demo sample application is included with the OpenLink installation and provides an interactive interface to test ODBC connections and execute SQL queries against your JDBC data source.
Launch and Connect
Launch the C++ Demo from the Start Menu. Select Environment → Open Connection, choose your new DSN, and enter your credentials.

Execute SQL Queries
Select SQL → Execute SQL from the menu to enter and execute SQL queries. Successful results confirm that the ODBC-to-JDBC Bridge is functioning correctly.

Technical Glossary
Data Source Name (DSN)
A data structure that contains the information required for an application to connect to a specific database.
Request Broker
A server-side component of the OpenLink Multi-Tier architecture that manages client connections and routes requests to the appropriate database agent.
Bridge Agent
A component that acts as a bridge between different database connectivity standards, in this case, translating ODBC calls to JDBC calls.
CLASSPATH
An environment variable that tells the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) where to find class libraries, including the JDBC driver JAR files.
Frequently Asked Questions
A 64-bit Java Virtual Machine (JVM) must be installed and configured on the machine where the driver will be installed. This is essential for the bridge to function properly.
The JDBC driver .jar file must be installed on the same machine as the OpenLink Request Broker and Bridge Agent, and included in the CLASSPATH environment variable so the JVM can locate it.
The license files (e.g., oplrqb.lic, jdbc.lic) must be placed in the {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin directory.
You can edit the {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin/oplrqb.ini file and set variables like CLASSPATH in the [Environment JDBC18] section of the OpenLink Rule Book.