Why Use an ODBC-to-JDBC Bridge?
This guide addresses a common and critical scenario: your target data source offers only a JDBC driver for connectivity, but your client application is built to use ODBC. The OpenLink ODBC-to-JDBC Bridge seamlessly translates between these two standards, unlocking access that would otherwise be impossible. The Lite Edition provides this core functionality with the following advantages:
Direct & Simple Connectivity
The single-tier architecture loads directly into your application's process space. There are no separate server components to install or manage, simplifying setup and reducing complexity.
Universal JDBC Compatibility
Unlock access to any JDBC-compliant data source from your existing ODBC applications. The bridge ensures broad compatibility with a wide range of modern databases and data sources.
High-Performance Bridging
Benefit from an efficient, in-process translation between ODBC and JDBC API calls. This direct bridging architecture ensures minimal performance overhead for your data access operations.
Overview
The OpenLink Single-Tier 'Lite' Edition ODBC Driver for JDBC Data Sources (ODBC-JDBC Bridge) enables Windows applications to access JDBC-compliant data sources through the ODBC interface. This guide provides comprehensive installation and configuration instructions for Windows operating systems.
What is the ODBC-JDBC Bridge?
The ODBC-JDBC Bridge is a database driver that employs ODBC to connect to databases while providing a bridge between the JDBC and ODBC APIs. This allows applications designed for ODBC to seamlessly access JDBC data sources without modification.
Key Features
- Single-Tier architecture (no separate database server required)
- Universal support for any JDBC-compliant data source
- Full ODBC API compliance
- Support for both 32-bit and 64-bit Windows
- Advanced configuration options for performance tuning
Pre-Installation Requirements
System Requirements
- Operating System: Microsoft Windows (Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11 or Server editions)
- Processor: Intel-compatible processor with SSE2 support
- RAM: Minimum 1 GB (2 GB recommended)
- Disk Space: Minimum 500 MB for installation
Software Requirements
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): A compatible JVM matching the driver bitness (32-bit or 64-bit)
- JDBC Driver: The JDBC driver for your target database
- Administrator Privileges: Required for driver installation
Configuration Requirements
Before configuration, you must have:
- JDBC Driver Information: The driver class name and connection URL
- Database Credentials: Username and password for your database
- Environment Variables: Knowledge of PATH and CLASSPATH configuration
Installation Steps
Launch the Installer
Locate and double-click the OJDBC installation executable to launch the installer.
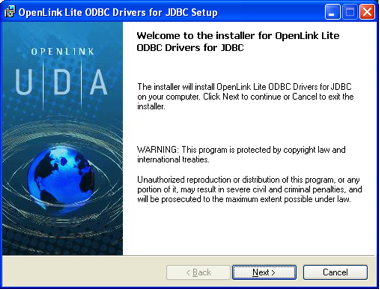
Welcome Screen
The Welcome screen presents an overview of what will be installed. Click "Next >" to continue.
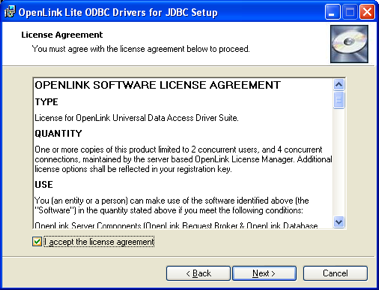
License Agreement
Read the License Agreement carefully. You must accept the terms to continue. Select "I Agree" and click "Next >".
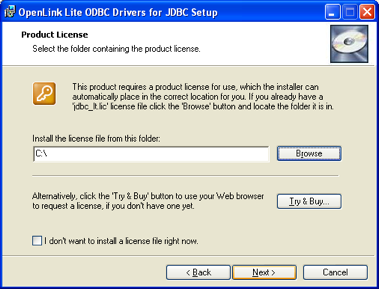
Licensing Information
Enter your licensing details if applicable. For evaluation versions, this may be optional. Click "Next >".
Installation Options
Choose whether to install to the default location or specify a custom path. Standard installation is recommended.
Begin Installation
Review your settings and click "Install" to begin copying files to your system.
Installation Complete
Once installation is complete, click "Finish" to close the installer.
Java Environment Setup & JDBC Testing
Proper Java configuration is critical for the ODBC-JDBC Bridge to function correctly. This section covers environment setup and includes a complete JDBC testing utility to verify your configuration before proceeding to ODBC setup.
Locate the JVM
Find the jvm.dll file location in your Java installation. Typically located at:
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_version\jre\bin\server\jvm.dll
C:\Program Files (x86)\Java\jre1.8.0_version\bin\server\jvm.dllConfigure PATH Environment Variable
Add the directory containing jvm.dll to your system PATH:
- Open System Properties (Win+Pause or Control Panel → System)
- Click "Advanced system settings" then "Environment Variables"
- Under "System variables", edit "Path" and add a new entry for
C:\path\to\jvm\bin\server - Click OK and restart your applications
Locate JDBC Driver
Find the JDBC driver .jar file for your target database. For example:
C:\Program Files\JDBC Drivers\postgresql-42.2.14.jar
C:\Program Files\JDBC Drivers\mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jarConfigure CLASSPATH Environment Variable
Add the JDBC driver .jar file to your system CLASSPATH:
- Open Environment Variables and click "New" under "System variables".
- Set Variable name:
CLASSPATH - Set Value:
C:\path\to\jdbc\driver.jar - For multiple drivers, separate paths with semicolons (
;).
Optional - Configure JVM Options
Set the OPL_JVM_OPTS environment variable for custom JVM parameters:
Variable name: OPL_JVM_OPTS
Value: -Xms64m -Xmx512mVerify Java Installation
Test your Java setup by running these commands in Command Prompt:
java -version
javac -versionBoth commands should display version information without errors.
JDBC Testing Utility - UniversalJDBCTest
Before configuring the ODBC DSN, verify your JDBC driver is properly installed and your
connection parameters are correct using this testing utility. Copy the code into a file named
UniversalJDBCTest.java, edit the connection parameters, then compile and run.
import java.sql.*;
public class UniversalJDBCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// EDIT THESE VALUES
String driverClass = "org.postgresql.Driver";
String jdbcURL = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb";
String username = "myuser";
String password = "mypassword";
try {
System.out.println("Loading JDBC Driver: " + driverClass);
Class.forName(driverClass);
System.out.println("Connecting to: " + jdbcURL);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcURL, username, password);
System.out.println("Connection successful!");
DatabaseMetaData meta = conn.getMetaData();
System.out.println("Database: " + meta.getDatabaseProductName() + " " + meta.getDatabaseProductVersion());
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("ERROR: Connection failed!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Compile and Run:
javac UniversalJDBCTest.java
java UniversalJDBCTestA successful test confirms your Java and JDBC driver setup is correct.
ODBC DSN Configuration
After installation, configure a Data Source Name (DSN) to establish connections through the ODBC-JDBC Bridge.
Open ODBC Administrator
Access the ODBC Data Source Administrator. On Windows, open Control Panel → Administrative Tools → ODBC Data Sources (32-bit or 64-bit as appropriate).

Navigate to System DSN Tab & Add
Click on the "System DSN" tab and click the "Add..." button to create a new data source.
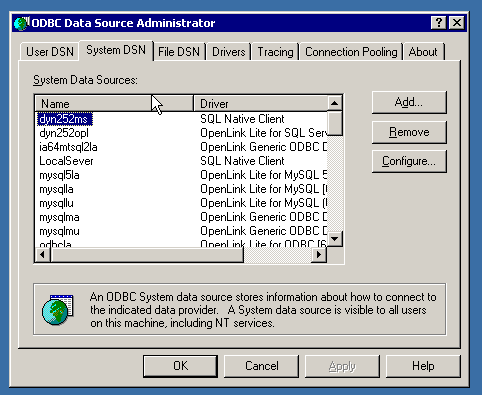
Select Driver
Select the "OpenLink JDBC Lite Driver" from the list of available drivers.
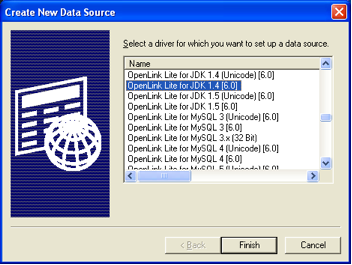
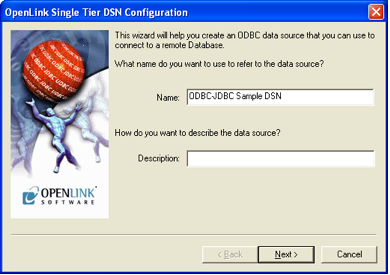
Configure DSN Name
Enter a descriptive name for your data source (e.g., "MyVirtuoso", "OracleDB_DSN").
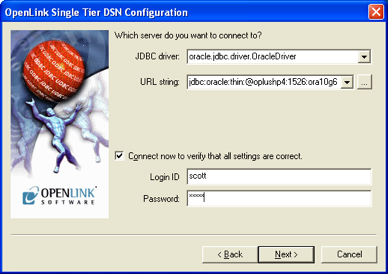
Connection Tab Settings
Configure the connection parameters. Enter the JDBC driver class, URL string, username, and password for your database connection.
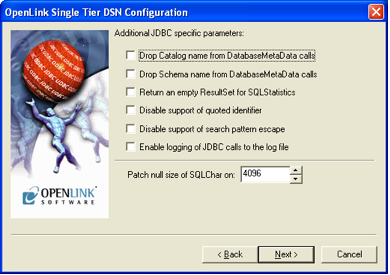
Database-Specific Settings
Configure database-specific parameters if needed. These settings allow fine-tuning of the connection.
Options Tab Configuration
The Options tab provides additional configuration parameters such as row buffer size and other performance-related settings.
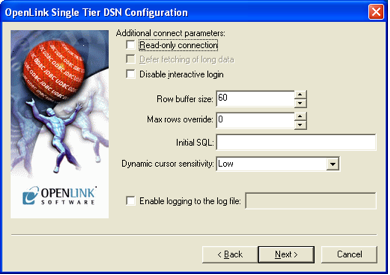
Compatibility Settings
Configure compatibility options to ensure optimal behavior with your specific applications and database.

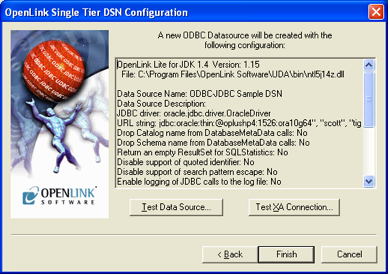
Test Connection
Click the "Test" button to verify that your configuration is correct and that the connection to your database is successful.
Technical Glossary
CLASSPATH
An environment variable that tells the Java Virtual Machine where to find the necessary class libraries, such as the JDBC driver .jar file.
DSN (Data Source Name)
A user-friendly name for an ODBC data source that stores connection details like driver name, server, and database.
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
An application programming interface (API) for the programming language Java, which defines how a client may access a database.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine)
An abstract computing machine that enables a computer to run a Java program, required for the ODBC-to-JDBC bridge to function.
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity)
A standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS).
ODBC Data Source Administrator
A Windows system tool used to manage ODBC data sources, drivers, and DSN configurations.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Single-Tier 'Lite' Edition ODBC Driver for JDBC Data Sources must match the bit format (32-bit or 64-bit) of the client application.
A compatible JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is required. For a 32-bit driver, a 32-bit JVM is needed, even on 64-bit Windows.
You must know the driver class name of your JDBC driver and the full details of the JDBC connection URL.
You must add the full directory path to the 'jvm.dll' to your system's PATH, and the full file path to the JDBC driver's .jar file to your system's CLASSPATH.
It is used to provide a list of special JVM command line arguments (e.g., -Xms64m) to be passed to the JDBC Driver on connect.
This guide is semantically enriched with structured metadata. View the Knowledge Graph representation: ODBC-JDBC Bridge Installation Guide on URIBurner