Overview
This installation guide walks you through the installation of the Enterprise Edition ODBC to ODBC Bridge Driver to a Personal or Application Server host functioning as a client to a database that's accessible via its native ODBC Driver.
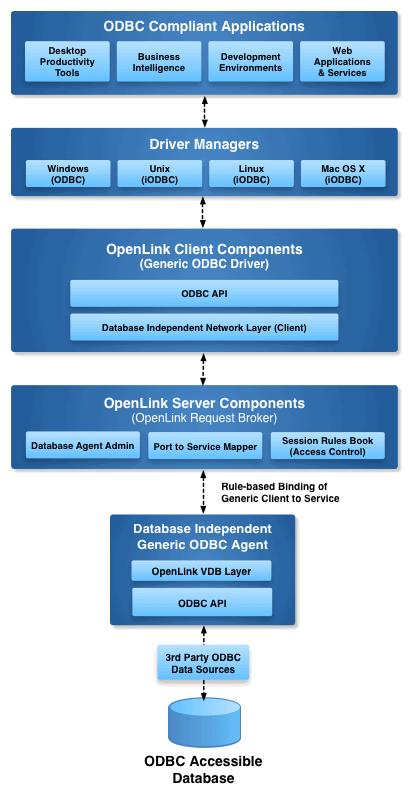
Why OpenLink ODBC to ODBC Bridge?
While basic connectivity enables database access, it doesn't address the data security, privacy, and administrative architecture challenges facing modern enterprises. OpenLink's ODBC to ODBC Bridge Connector solves this with:
Fine-Grained Access Control
Powerful attribute-based access controls (ABAC) as ODBC session-level enforcers of data access policies, aligned with governance requirements and compliance standards.
Enhanced Data Security
Comprehensive protection mechanisms addressing data security and privacy challenges, ensuring sensitive information is protected at the session level.
Deployment Flexibility
Flexible topology options essential for managing large-scale ODBC-based client applications and services in enterprise environments.
System Requirements
Before beginning the installation process, ensure your system meets the following requirements:
Minimum Specifications
- Operating System: Linux (x86_64), Unix, or compatible POSIX-compliant system with glibc 2.5 or later
- Memory: Minimum 256 MB RAM; 512 MB or more recommended for production environments
- Disk Space: At least 200 MB free space for installation and runtime components
- ODBC Drivers: Third-party or native ODBC drivers matching your target database platform
- Permissions: Root or sudo access required for system-wide installation and service management
- Network: Open ports for OpenLink broker communication (default port 5000)
1Download the Installer Archive
Option A: Using the OpenLink Download Page
- Visit the OpenLink ODBC Enterprise Edition Driver Download Page to download the appropriate ODBC to ODBC Bridge Driver.
Option B: Using curl Command
Alternatively, use curl to download the installer archives and install.sh script directly:
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/misc/install.sh
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/9.0/x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25-64/oplodbc.taz
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/9.0/x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25-64/odbc_mv.taz
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/9.0/x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25-64/oplrqb.taz
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/9.0/x86_64-generic-linux-glibc25-64/odbc_admin.taz2Pre-Installation Configuration
Third-Party ODBC Drivers
You must possess third-party or native ODBC drivers that connect to your target data source. A client portion of these drivers must be installed on the same machine as the Multi-Tier "Enterprise" Edition Request Broker and Bridge Agent(s) for ODBC Data Sources.
- The ODBC driver library file (or a symbolic link to it) must be included in the active shared library environment variable (e.g.,
LD_LIBRARY_PATH,LIBPATH,SHLIB_PATH). - Supporting libraries (or links to them) may also need to be included in this variable value.
Bit Format Compatibility
You must know whether the local ODBC components are 32-bit or 64-bit. The Multi-Tier server components must match the bit format of the local ODBC components, not the OS.
file /path/to/odbc/driver.so
3Installation
- Log onto the target machine for the installation and create a suitable OpenLink installation directory
{OPENLINK_INSTALL}. - Copy all the downloaded components to the
{OPENLINK_INSTALL}directory, which are theinstall.sh,oplrqb.taz,oplodbc.taz,odbc_admin.taz,odbc_mv.tazfiles. - Install OpenLink components using the
install.shshell script with the command:sh install.sh - Take care to enter correct information when prompted pertaining to ports, passwords, etc. and ensure that you note these down for future use.
- The installation should finish without error.
4Configuration
- To setup the OpenLink environment, from the
{OPENLINK_INSTALL}directory run the command:. ./openlink.sh - Open the file
{OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin/oplrqb.iniwith a suitable text editor such asvi. - Place the License file(s) (
oplrqb.lic,odbc.lic) either purchased or obtained during the evaluation download process in the{OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bindirectory. - Start the OpenLink License Manager (
oplmgr) by going to the{OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bindirectory and running the command:./oplmgr +start - Start the OpenLink Request Broker (
oplrqb) by going to the{OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bindirectory and running:./oplrqb -v ;;; To start in background mode or ./oplrqb -fd ;;; To start in foreground debug mode
-v flag for production environments (background mode) and -fd for troubleshooting (foreground debug mode).
5Create Data Source Name (DSN)
- Open the file
{OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin/odbc.iniwith a suitable text editor such asvi. - Locate and edit the sample OpenLink Multi-Tier ODBC data source (DSN) called
[OpenLink]created during the installation process and edit as follows:[OpenLink] Driver = {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/lib/oplodbc.so ServerType = Odbc Host = localhost:5000 ;;; replace "localhost" with the hostname Database = {Third Party ODBC DSN Name} Options = Username = {username} Password = {optional password} FetchBufferSize = 99 ReadOnly = no DeferLongFetch = no JetFix = no WideAsUTF16 = Y Description = Sample Multi-Tier Connection
- Host: Replace "localhost" with the actual hostname if the broker runs on a different machine
- Database: Enter the name of your third-party ODBC DSN
- Username/Password: Provide credentials for the target database
- WideAsUTF16: Set to Y for unixODBC compatibility
6Test Connection
Using iODBC Runtime Environment
Use the OpenLink iODBC iodbctest sample tool to make a test connection:
$ cd {OPENLINK_INSTALL}
$ . ./openlink.sh
$ iodbctest "DSN=OpenLink;UID={username};PWD=xxxxxxxx"
iODBC Demonstration program
This program shows an interactive SQL processor
Driver Manager: 03.52.0507.0105
Driver: 08.02.1217 OpenLink Generic ODBC Driver (oplodbc.so)
SQL>SQL statements can now be issued directly against the target database from the SQL> prompt:
SQL> select count(*) from orders
(count(*))
-----------------
23
result set 1 returned 1 rows.
SQL>Using unixODBC Runtime Environment
When using the unixODBC Driver Manager, ensure the WideAsUTF16 = Y parameter is in your DSN:
$ isql OpenLink {username} {password}
+---------------------------------------+
| Connected! |
| |
| sql-statement |
| help [tablename] |
| echo [string] |
| quit |
| |
+---------------------------------------+
SQL> select count(*) from orders
+------------------+
| (count(*)) |
+------------------+
| 23 |
+------------------+
SQLRowCount returns -1
1 rows fetched
SQL>Glossary of Terms
This section defines key technical terms and components related to the OpenLink ODBC to ODBC Bridge Driver installation and configuration.
ODBC
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard C-language application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS). It provides a standardized way for applications to access different databases regardless of the database vendor.
DSN
Data Source Name (DSN) is a data structure that contains the information about a specific database that an ODBC driver needs in order to connect to it. DSNs are typically stored in configuration files like odbc.ini and define connection parameters such as host, port, username, and database name.
Request Broker
The OpenLink Request Broker (oplrqb) is a core Multi-Tier component that listens for client connection requests and routes them to an appropriate database agent. It acts as a central hub for managing connections in the multi-tier architecture.
License Manager
The License Manager (oplmgr) is an OpenLink component responsible for managing and validating license files. It must be running before the Request Broker can start, as the broker checks for valid licenses on startup.
iODBC
iODBC is an open-source ODBC driver manager for non-Windows platforms (primarily Unix/Linux), providing an implementation of the ODBC API. It allows applications to use ODBC to access databases on systems where the Windows ODBC driver manager is not available.
unixODBC
unixODBC is an open-source project that provides an implementation of the ODBC API for non-Windows platforms, including a driver manager and associated tools like isql. It's widely used on Linux systems as an alternative to iODBC.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH
LD_LIBRARY_PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like systems that specifies a list of directories where the dynamic linker should look for shared libraries at runtime. Adding ODBC driver paths to this variable ensures they can be found by the OpenLink driver.
Bridge Agent
The Bridge Agent is the server-side component that communicates with the target database's native ODBC driver. It receives requests from the Request Broker and executes them against the local third-party DSN, effectively acting as a bridge between the OpenLink protocol and the native ODBC driver.
Multi-Tier Architecture
Multi-Tier is an architecture where a client, a middle-tier service (like the Request Broker), and a database server are distinct components, often running on separate machines. This architecture enhances scalability, flexibility, and allows for bit-format mixing (32-bit clients with 64-bit backends, or vice versa).
Enterprise Edition
The Enterprise Edition of the OpenLink ODBC to ODBC Bridge Driver is the production-grade version designed for high-performance, mission-critical deployments. It includes advanced features like connection pooling, load balancing, and comprehensive security options.
WideAsUTF16
WideAsUTF16 is an ODBC configuration parameter used with unixODBC to specify how wide character (Unicode) data should be handled. Setting WideAsUTF16 = Y ensures proper UTF-16 encoding compatibility with applications built using the unixODBC SDK.
ODBC-to-ODBC Bridge
An ODBC-to-ODBC Bridge is a connection mechanism that allows ODBC-compliant applications to access remote databases through their native ODBC drivers. The OpenLink implementation provides a Multi-Tier solution that enables connectivity across networks, platforms, and architectural boundaries.
Frequently Asked Questions
You can download the driver from the official OpenLink ODBC Enterprise Edition Driver Download Page . Alternatively, you can use curl to download the installer archives directly from the command line using the download links provided in Step 1.
You must have the third-party or native ODBC drivers for your target database already installed. The library file for this driver must be included in your system's shared library path (e.g., LD_LIBRARY_PATH). Additionally, ensure you have the appropriate read/write permissions for the installation directory.
No, the bit-format (32-bit or 64-bit) of the OpenLink Multi-Tier server components must match the bit-format of the local third-party ODBC components, not the operating system. This allows you to run a 32-bit ODBC driver on a 64-bit OS by using 32-bit OpenLink components.
After copying all downloaded files to an installation directory, run the command sh install.sh to begin the installation process. Follow the prompts, providing the requested information such as port numbers and administrative passwords.
From within the installation directory, you must source the environment script by running the command: . ./openlink.sh. This sets up all necessary environment variables for the OpenLink components to function correctly.
The license files (e.g., oplrqb.lic, odbc.lic) must be placed in the {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin directory. After placing the license files, restart the License Manager and Request Broker to activate the licenses.
Navigate to the {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin directory and run ./oplrqb -v to start it in the background, or ./oplrqb -fd to start it in foreground debug mode. The default port for the Request Broker is 5000.
You need to edit the {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin/odbc.ini file to configure a DSN for the ODBC-to-ODBC bridge. This is a standard ODBC configuration file used by both iODBC and unixODBC driver managers.
The 'Database' parameter should be set to the name of the third-party ODBC DSN that is configured on the same machine and connects to your target data source. This creates the bridge between the OpenLink driver and the underlying ODBC driver.
Yes, you must add the parameter WideAsUTF16 = Y to the target DSN in your odbc.ini file to ensure successful connections with applications built using the unixODBC SDK. This ensures proper Unicode character handling.
You can use the iodbctest utility with a connection string, for example: iodbctest "DSN=OpenLink;UID={username};PWD=xxxxxxxx". Once connected, you can issue SQL queries directly against your target database.
Ensure the ODBC driver library is installed and properly linked in your system's library path. Add the driver path to your LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/odbc/drivers:$LD_LIBRARY_PATHVerify that the Request Broker (oplrqb) is running and listening on the configured port. Check the status and review the broker logs:
ps aux | grep oplrqb
tail -f {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin/oplrqb.logEnsure license files (oplrqb.lic, odbc.lic) are placed in {OPENLINK_INSTALL}/bin directory. Restart the License Manager and Request Broker after adding licenses.
Download the OpenLink components matching your ODBC driver's bit format, not your OS architecture. Verify with: file /path/to/odbc/driver.so
Verify your DSN configuration in odbc.ini. Ensure the Database parameter references a valid third-party ODBC DSN that's configured on the same machine as the broker.
Add WideAsUTF16 = Y parameter to your OpenLink DSN in odbc.ini. This ensures proper character encoding compatibility with unixODBC-built applications.
An ODBC-to-ODBC Bridge allows an ODBC-compliant application on one machine to access a database on another machine via its own ODBC driver. It's useful for crossing network boundaries, connecting between different operating systems, or bridging between applications and databases with incompatible architectures.
Yes, this is a key use case. The Multi-Tier bridge allows a 32-bit client application to connect to the 32-bit OpenLink driver, which then communicates with the 64-bit Request Broker and Agent, which in turn uses the 64-bit native database driver.
The default port for the OpenLink Request Broker is 5000. This is configurable during the installation process and in the oplrqb.ini file. You can change this if port 5000 conflicts with other services on your system.