Overview
This installation guide walks you through the installation of the Lite Edition ODBC Driver for Microsoft SQL Server to a Personal or Application Server host functioning as a client to a SQL Server Database.

Installation Steps
Step 1: Download the Installer Archive
Visit the OpenLink ODBC Lite Edition Driver Download Page to download the appropriate ODBC driver for SQL Server.
Alternatively, curl can be used to download the installer directly:
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/10.0/x86_64-generic-win-64/wal10mzzz.msiStep 2: Run the Installer
Run the wal10mzzz.msi Windows MSI installer.
Step 3: Proceed
Select Next to proceed with the installation.
Step 4: License Agreement
Accept the License Agreement and click Next to proceed.
Step 5: License File Location
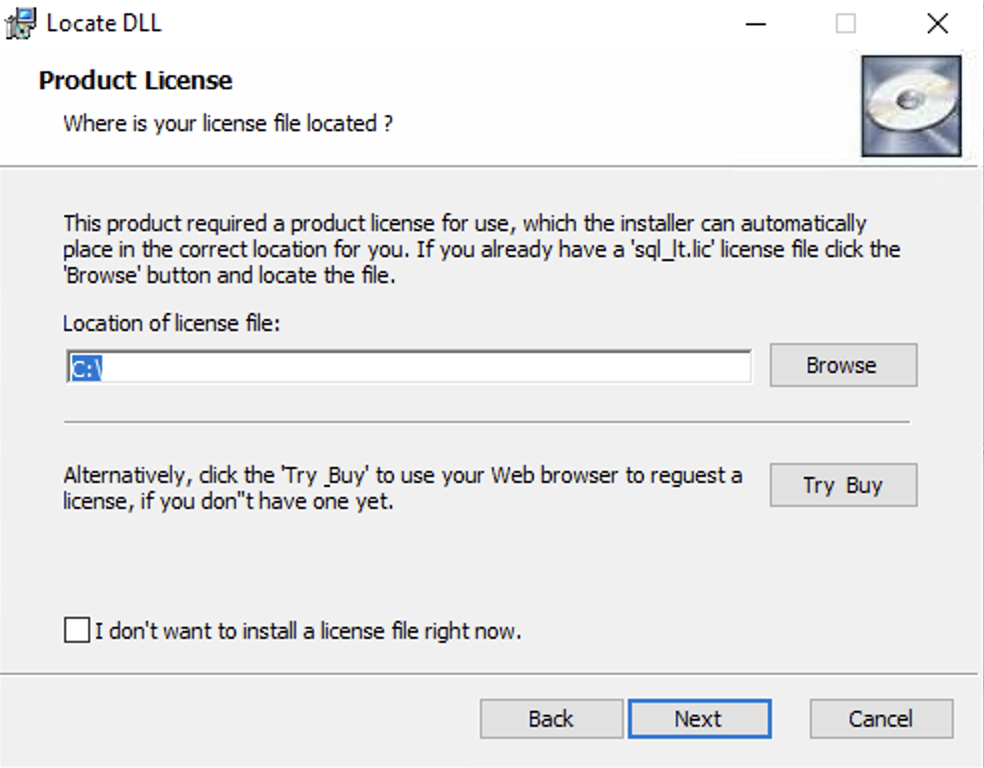
Select the location of the sql_lt.lic license for insertion in the correct location
during installation, or select the "I don't want to install a license file right now" check box
option to install later.
Step 6: Installation Type
Select the Complete or Typical installation to install in default location and go to Step 8, or Custom to choose custom components and location to perform the installation.
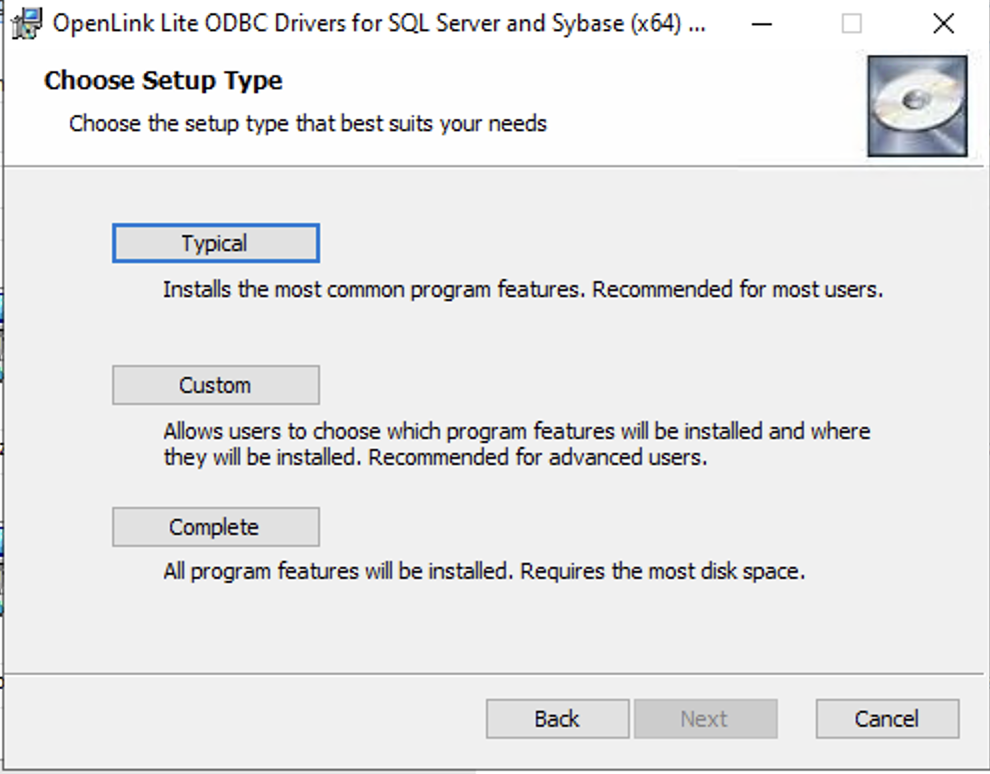
Step 7: Choose Components (Custom Install)
Choose what components to install and the location to install to.
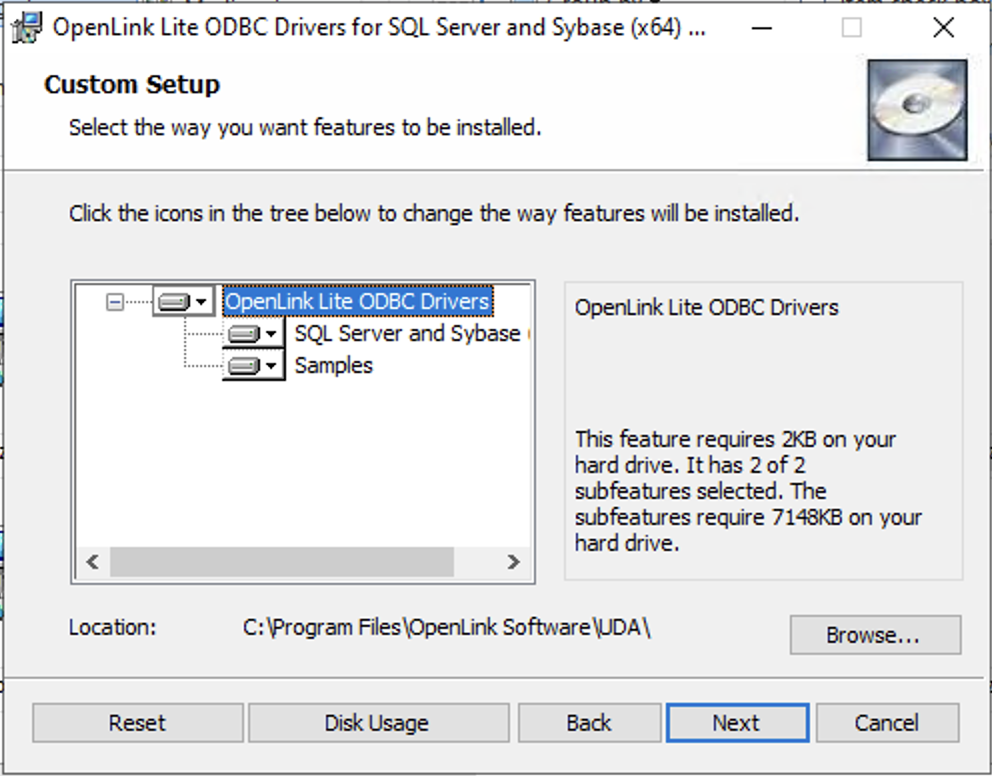
Step 8: Execute Installation
Click on the Install button to perform the installation.
Step 9: Progress
The installation is in progress.
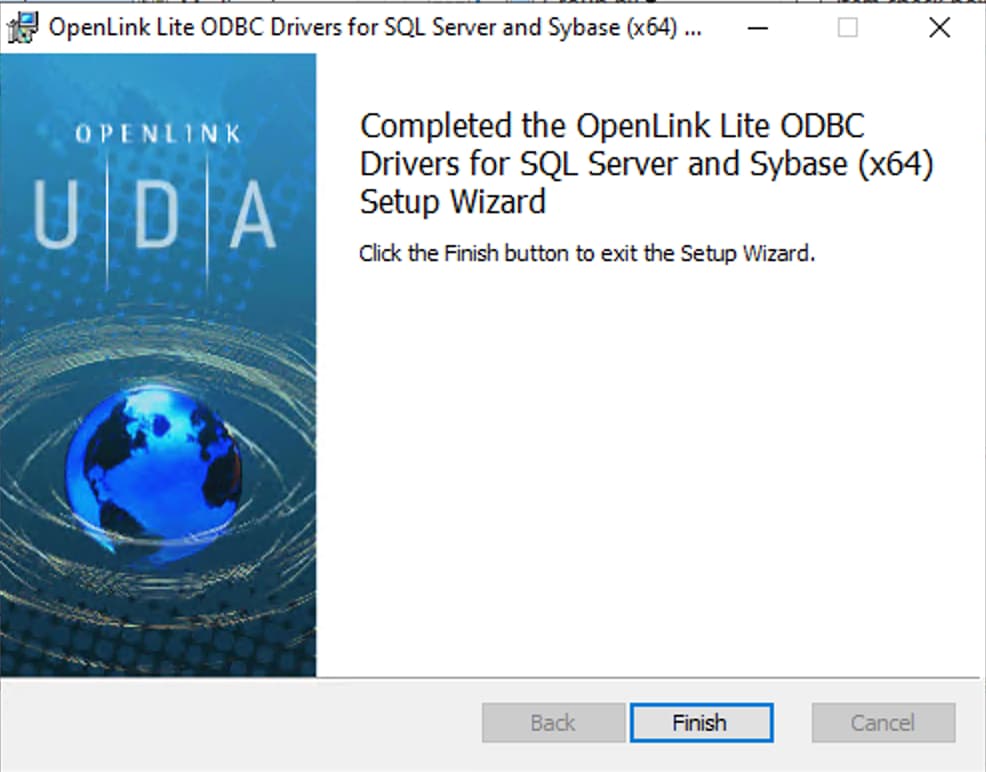
Step 10: Complete
The installation is complete. A reboot may be required to replace updated files or for other configuration changes to take effect.
Configuration
Follow these specific steps to configure the driver.
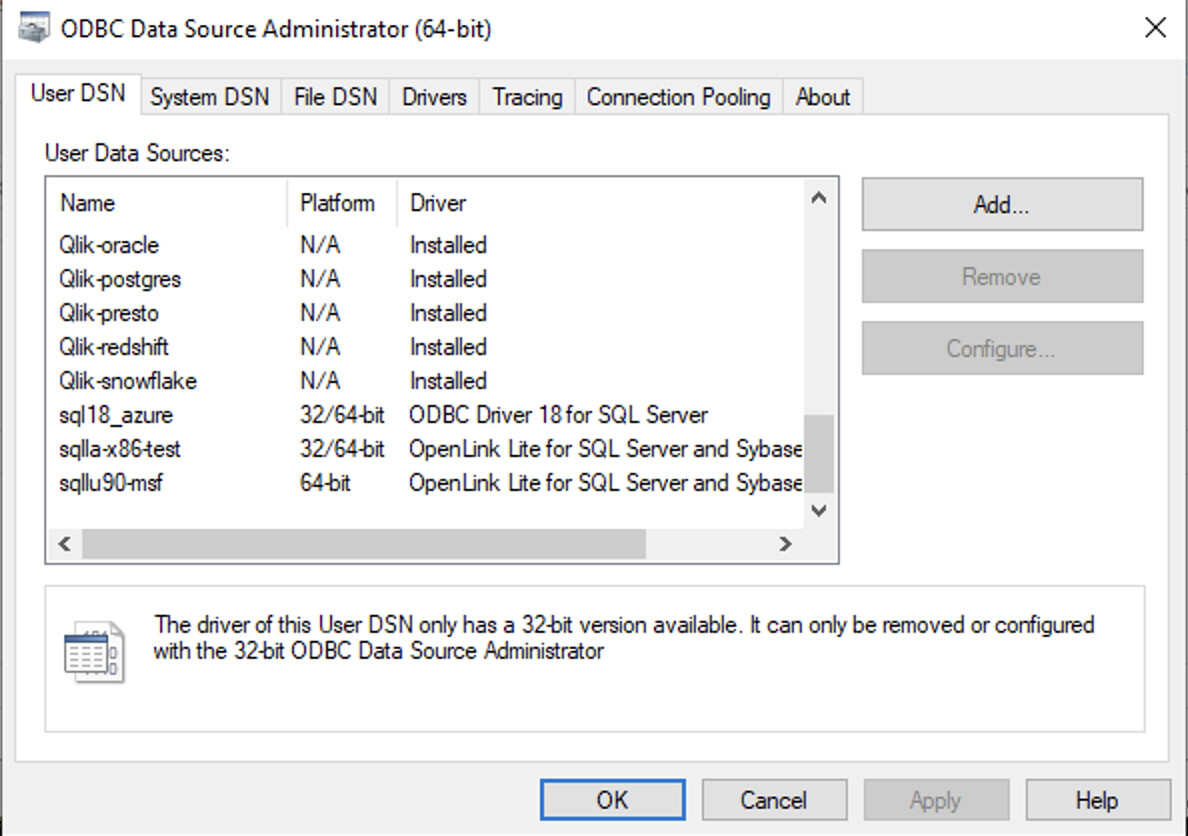
1. Open ODBC Administrator
Open the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator (64-bit) and click on the Add button to create an ODBC DSN.
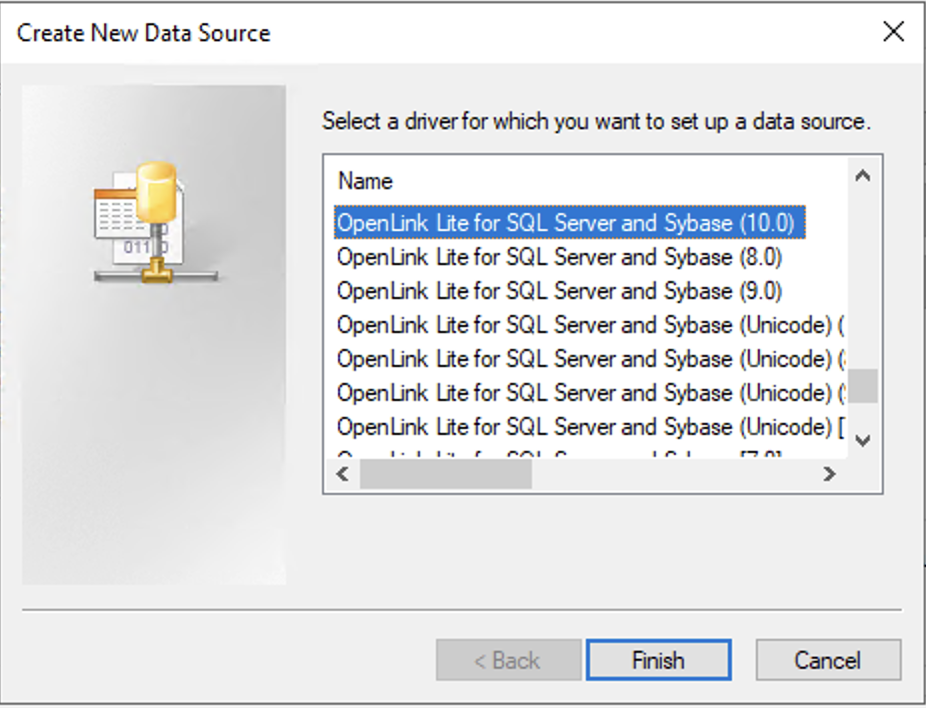
2. Select Driver
Select the OpenLink Lite for SQL Server and Sybase (10.0) ODBC driver.
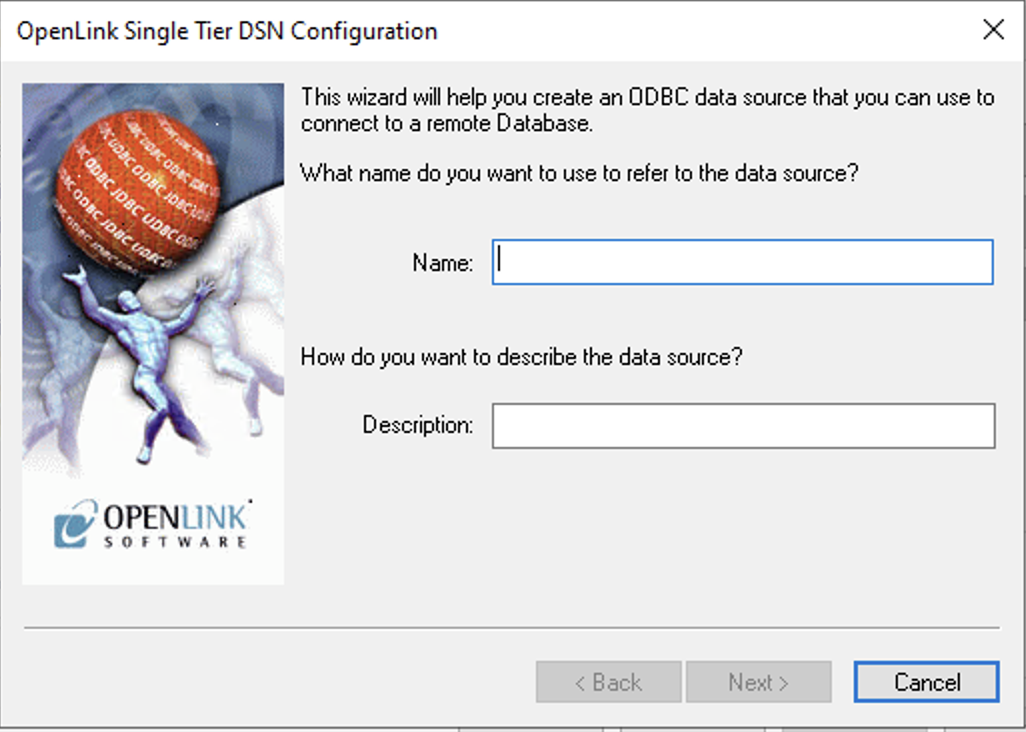
3. DSN Name
Enter an ODBC DSN Name and optional Description.
4. Host and Port
Choose Microsoft SQL Server as the database type and enter the Host Name and Port number of the target SQL Server instance.
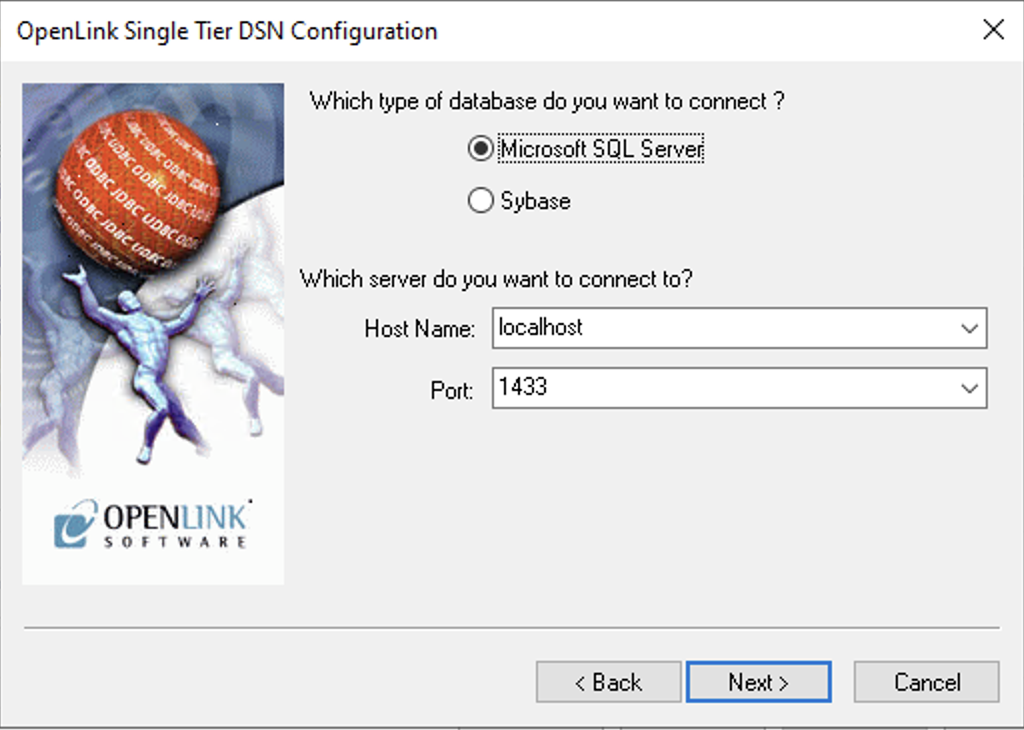
- Host Name
- The hostname or IP address on which Microsoft SQL Server listens.
- Port
- The TCP port on which Microsoft SQL Server listens (Default: 1433).
5. Authentication Method
Choose the SQL Server authentication method to be used:
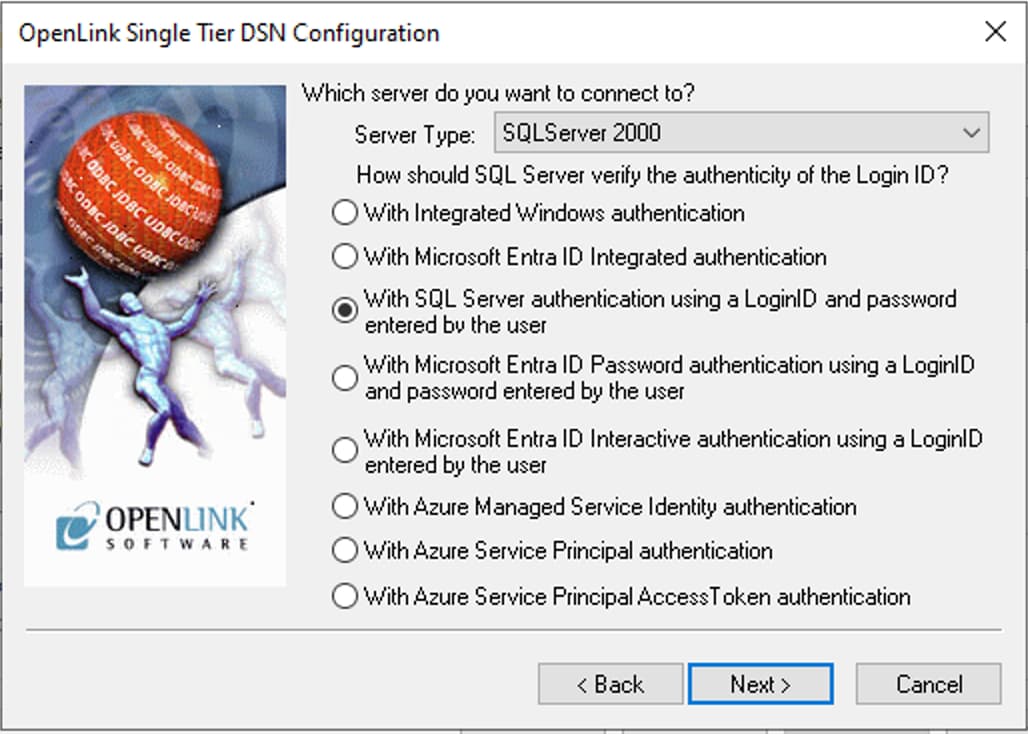
- With Integrated Windows authentication (ntlm)
- Specifies that the driver request a secure (or trusted) connection to a SQL Server using your Windows login.
- With Microsoft EntraID Integrated authentication
- Specifies that the driver authenticate to SQL Server using Microsoft Entra ID (ActiveDirectoryIntegrated).
- With SQL Server authentication (Default)
- Specifies that the driver authenticate using a login ID and password entered by the user.
- With Azure Service Principal authentication
- Authenticate using a Microsoft Entra service principal.
- With Azure Managed Service Identity
- Authenticate using a Managed Identity (ActiveDirectoryMsi).
6. Server Type
Choose the SQL Server Type to be connected to.
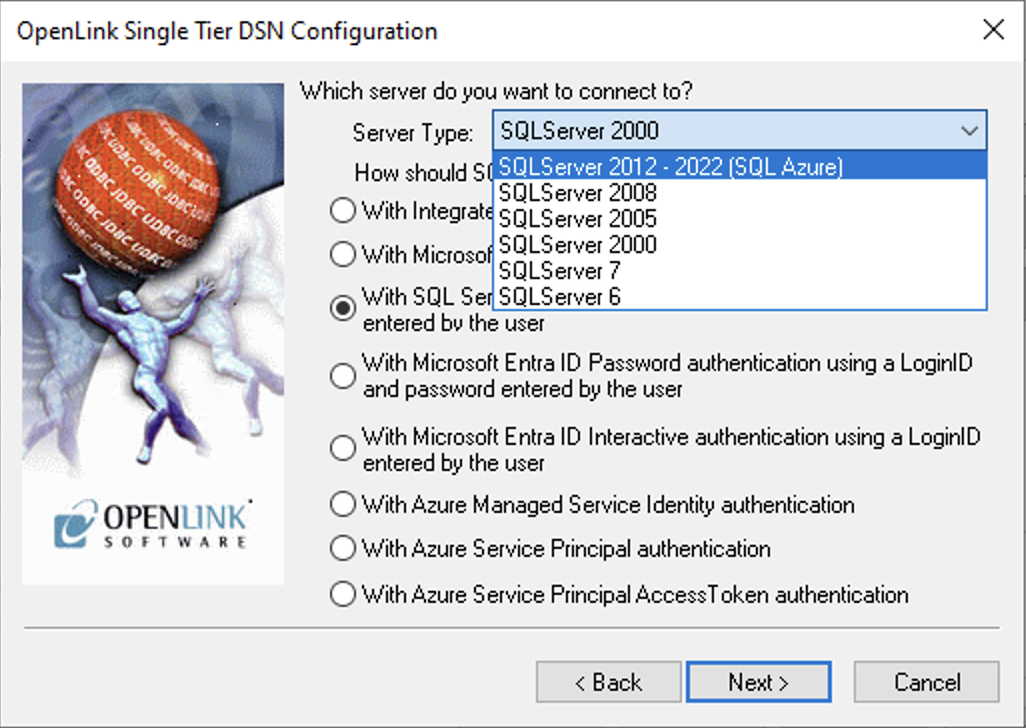
Server Type is an OpenLink proprietary parameter that associates the connection with a particular TDS version.
7. Connection Details
Enter the Instance Name, Mirror Host, Conn Timeout, and Use strong encryption if applicable. Select "Connect now" to verify settings, provide login details, and click Next.
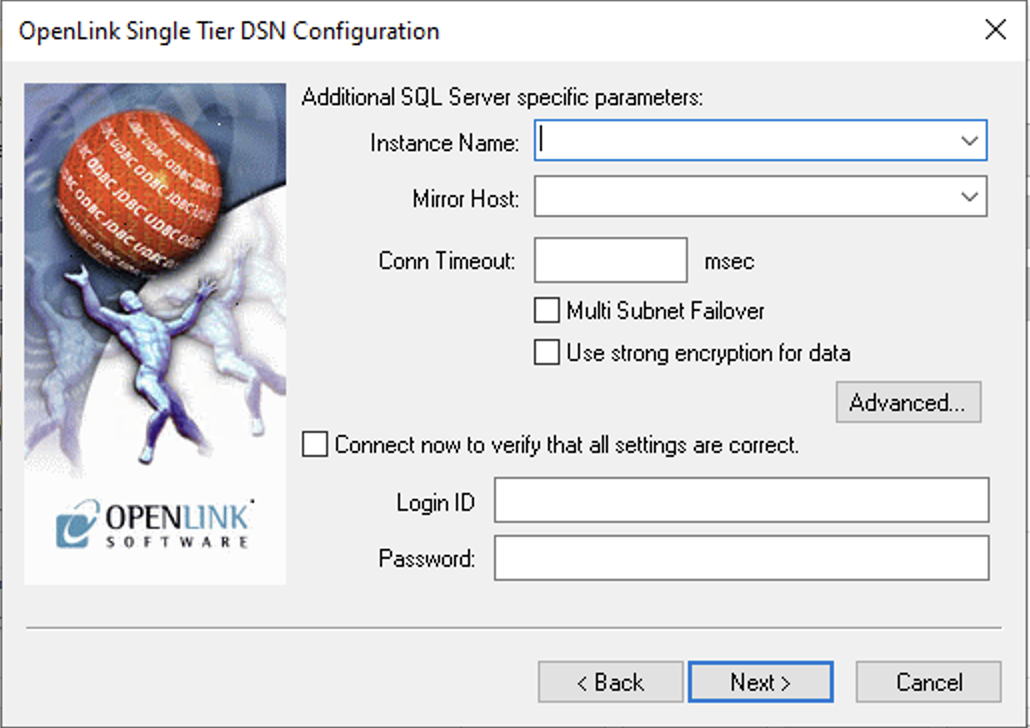
- Instance Name
- Microsoft SQL Server instance name. Can also be specified as
ServerName\InstanceName. - Mirror Host
- The name of the Failover Server hosting the mirrored database if configured.
- Use strong encryption of data
- Enable SSL encryption of data between driver and database.
- Multi Subnet Failover
- Switches ON SQL Server Multi Subnet Failover mode.
8. Advanced Options (Optional)
Use the Advanced button to configure advanced connection attributes if required.
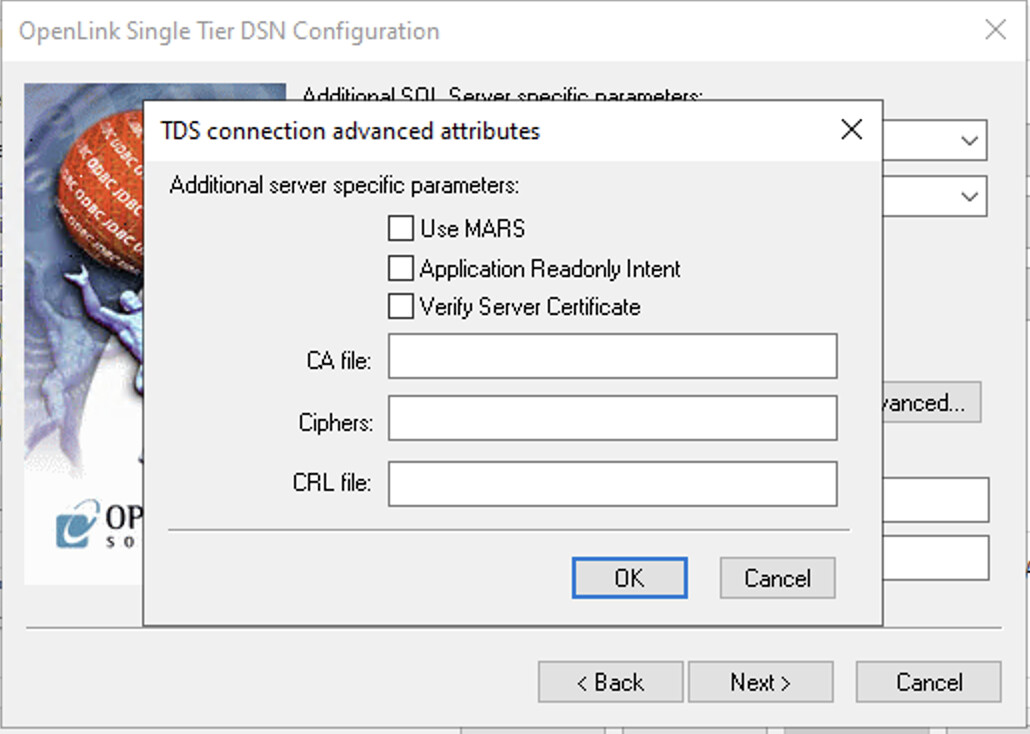
- Use Mars
- Multiple Active Result Sets enables concurrent processing of multiple queries on a single connection.
- Application Readonly Intent
- Requests connection to a read-only node in an Availability Group cluster.
- Verify Server Certificate / CA File
- Used to verify the database server SSL certificate against a CA file.
9. Database & Packet Size
Enter the Database, Character set, and Language or select from available items. Click Next.
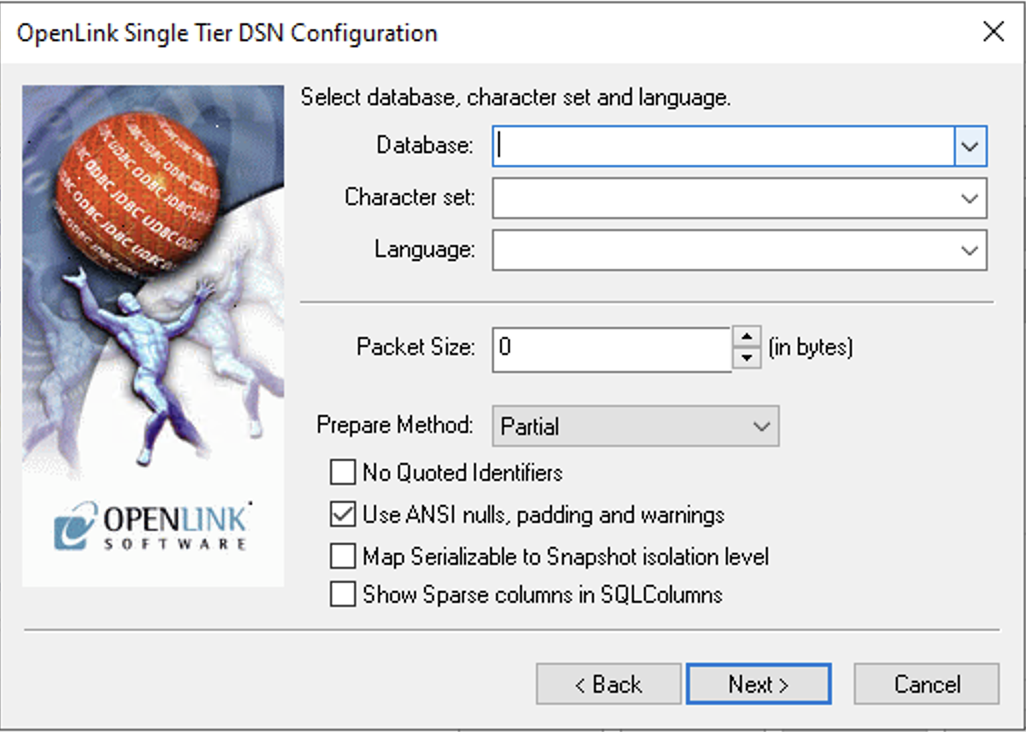
- Database
- The target Microsoft SQL Server database.
- Packet Size
- Determines bytes per network packet. 0 = default, -1 = max allowable. Correct setting can improve performance.
- Prepare Method
- Determines whether stored procedures are created for SQLPrepare calls (None, Partial, Full).
- No Quoted Identifiers
- Required for Jet engine based products like MS Access.
10. Cursors & Logging
Configure cursor and logging parameters (typically defaults are fine) and click Next.
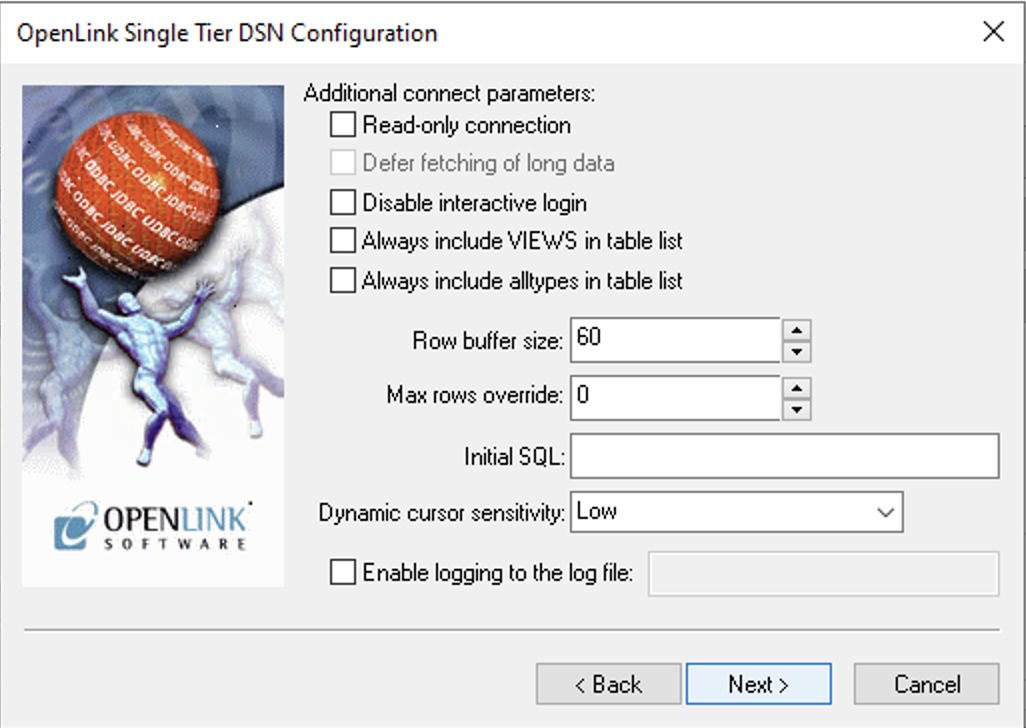
- Read-only connection
- Must be unchecked to INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE records.
- Defer fetching of long data
- Improves performance when queries do not include LONG data fields.
- Dynamic Cursor Sensitivity
- Enables/disables the row version cache used with dynamic cursors.
11. Compatibility Options
Configure compatibility options and click Next.
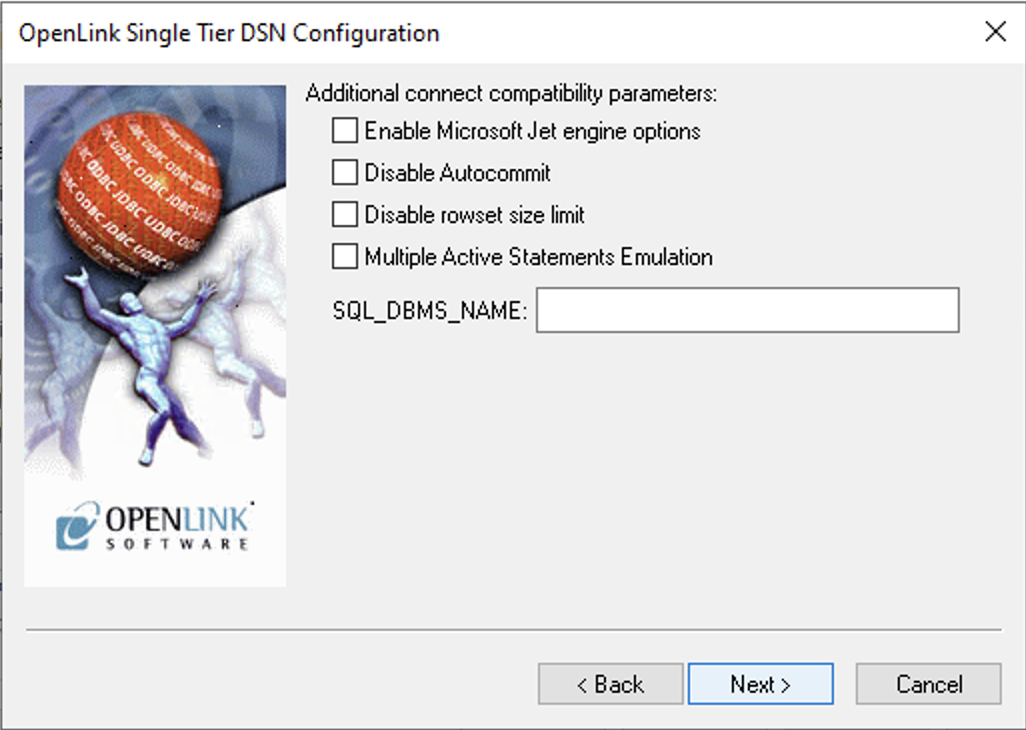
- Enable Microsoft Jet engine options
- Facilitates translation of data types for MS Access/Jet Engine.
- SQL_DBMS_NAME
- Manually overrides the response for products like Microsoft InfoPath (value should be "SQL Server").
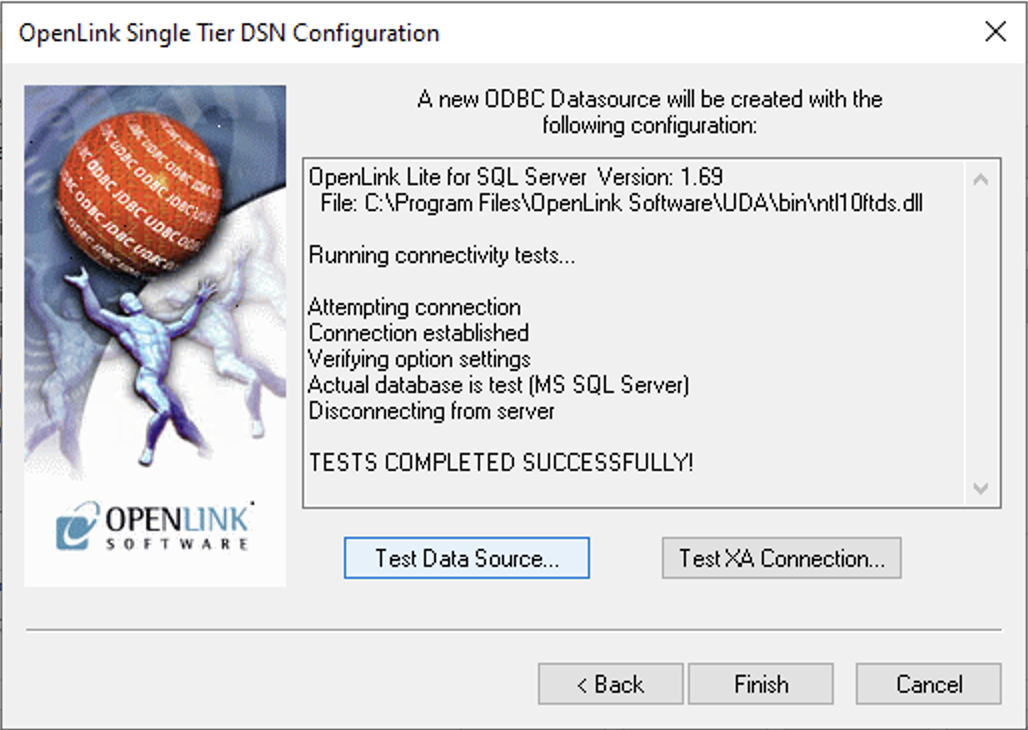
12. Test Data Source
Select the Test Data Source button to make a test connection to the database.
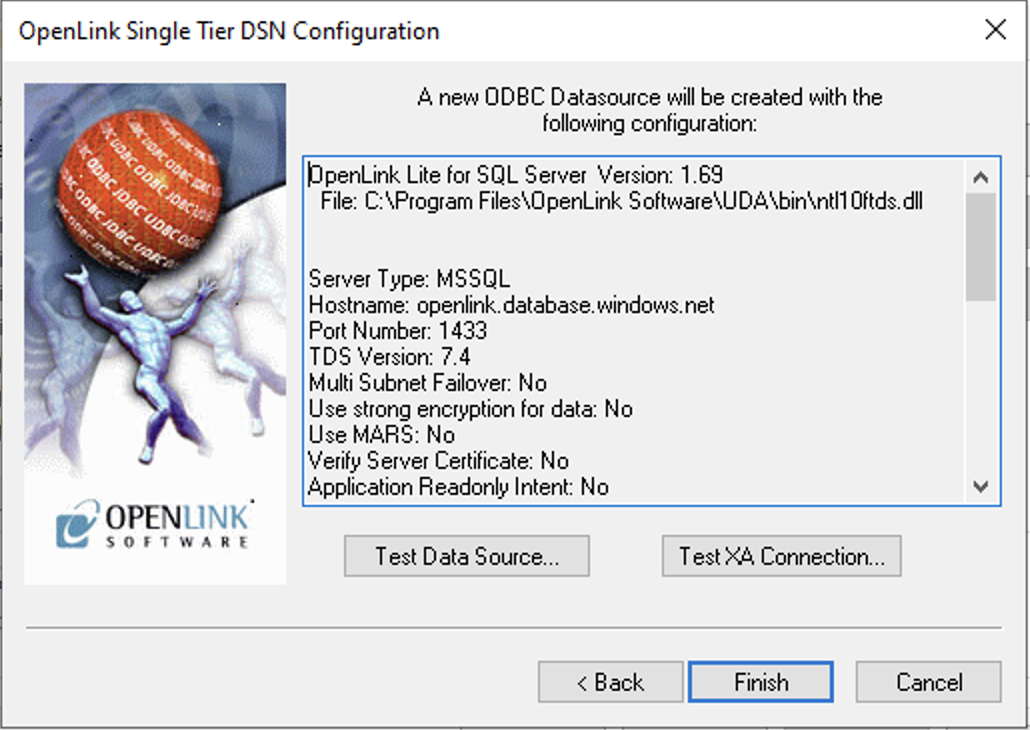
13. Success
The test connection should be successful.
C++ Demo Test Connection
Follow these steps to verify the connection using the provided C++ Demo application.
-
From the OpenLink Software program menu run the C++Demo sample application.
(Typically located atC:\Program Files\OpenLink Software\UDA\Samples\Odbc\cppdemo.exe)
-
Select the Environment -> Open Connection menu item.

-
Select the ODBC DSN to use.
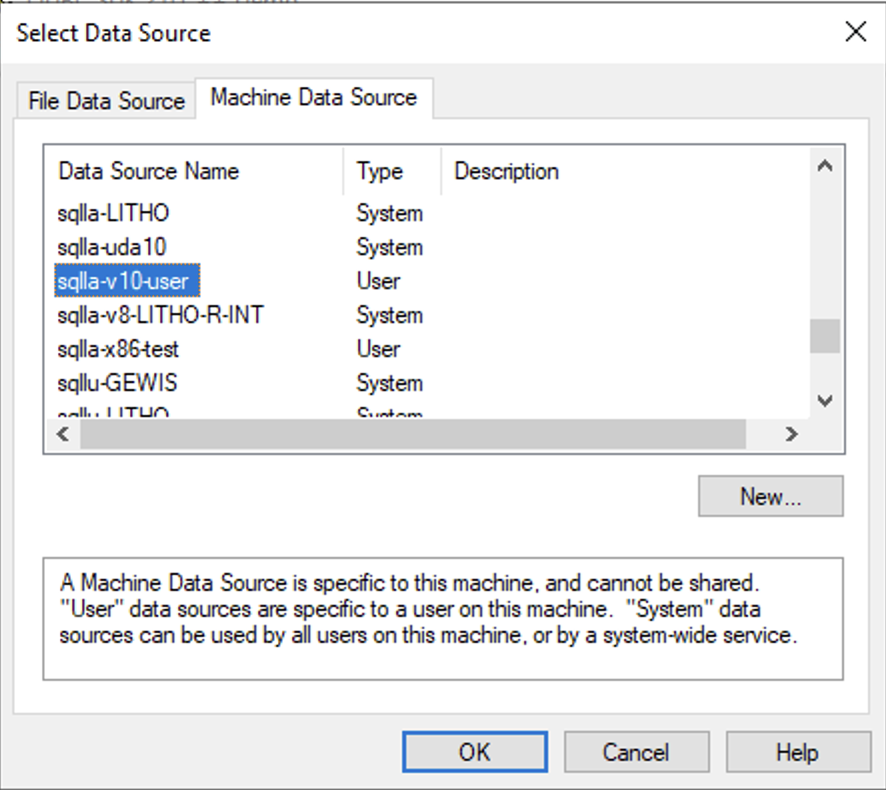
-
Enter login details for the target database.
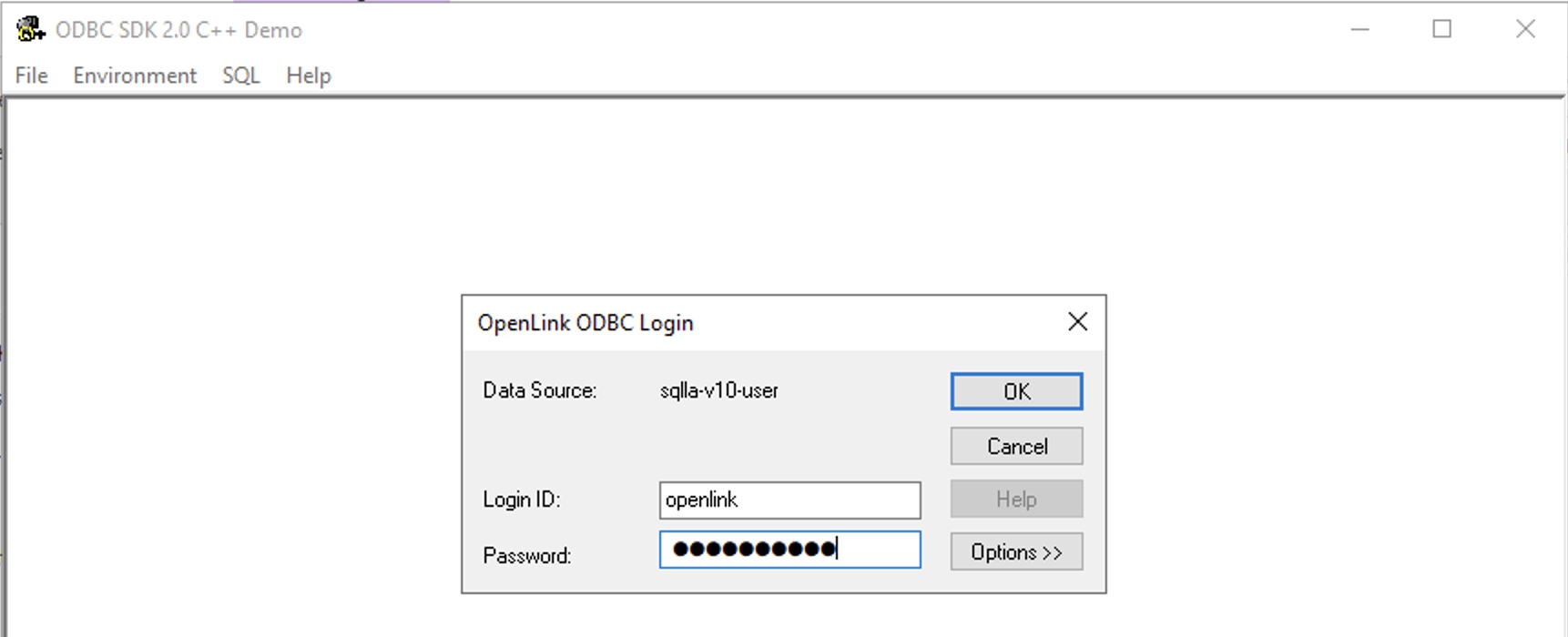
-
Select the SQL -> Execute SQL menu item.
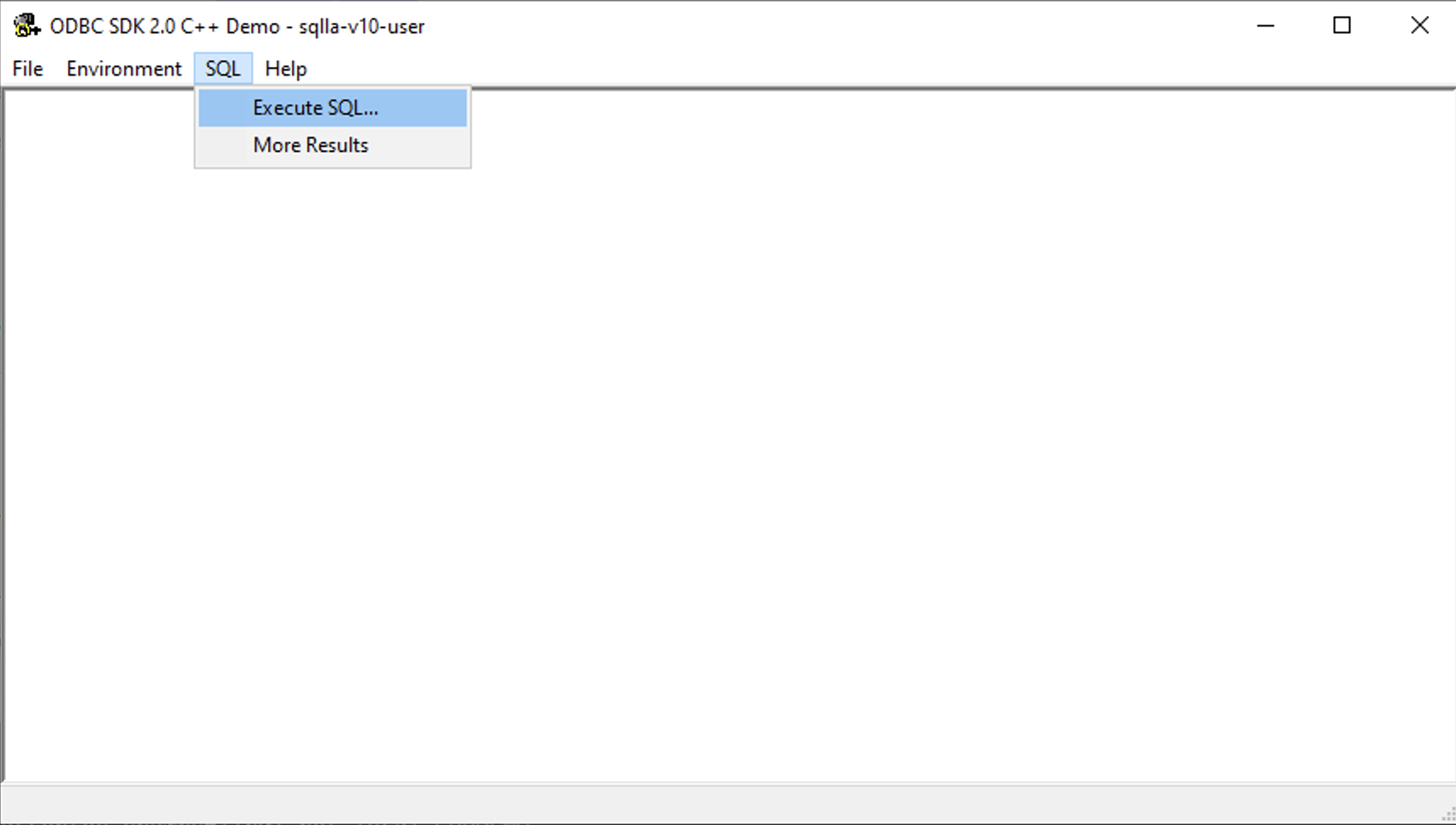
-
Enter a valid SQL query and click the OK button to run it.
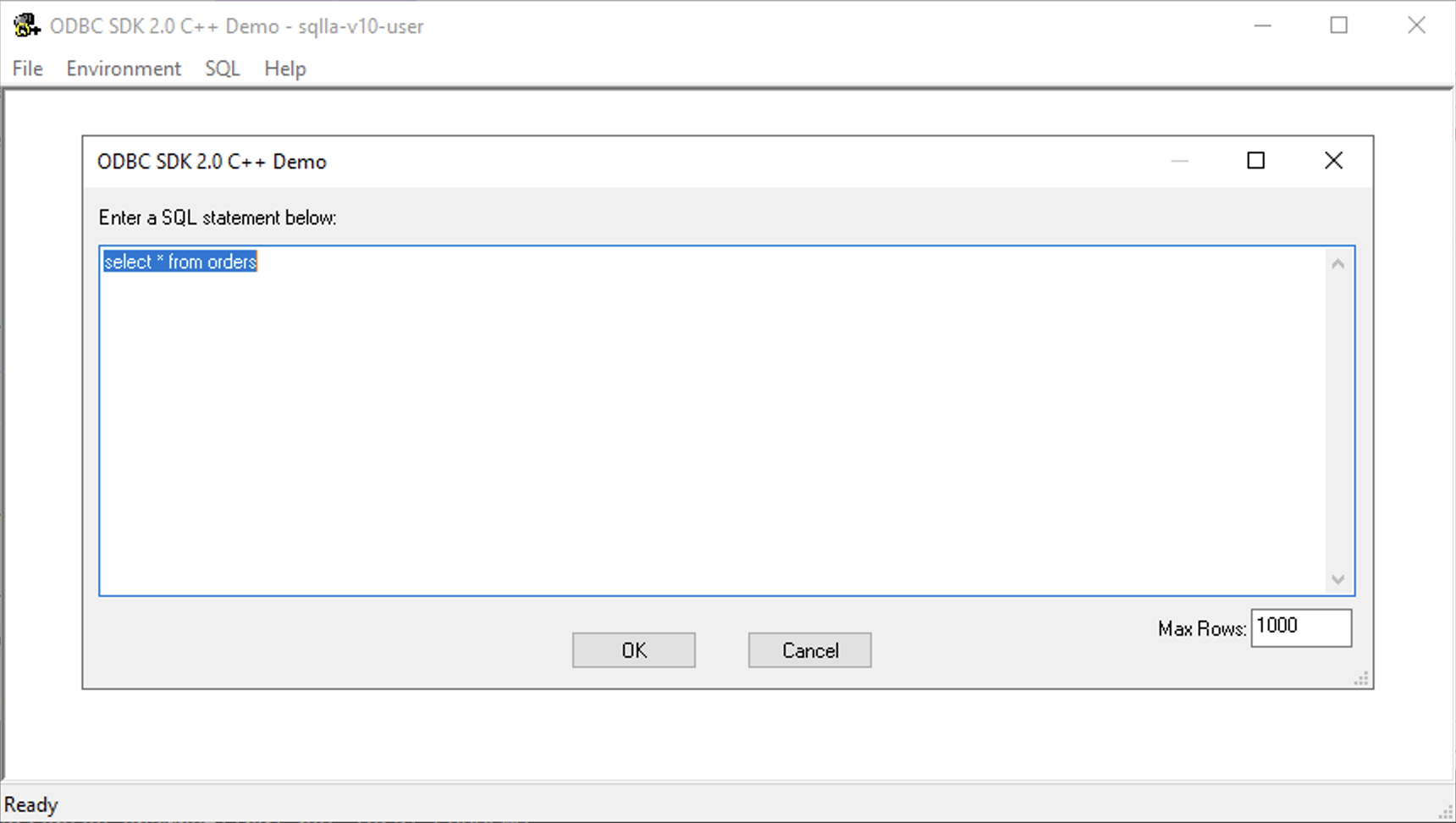
-
The query results are displayed.
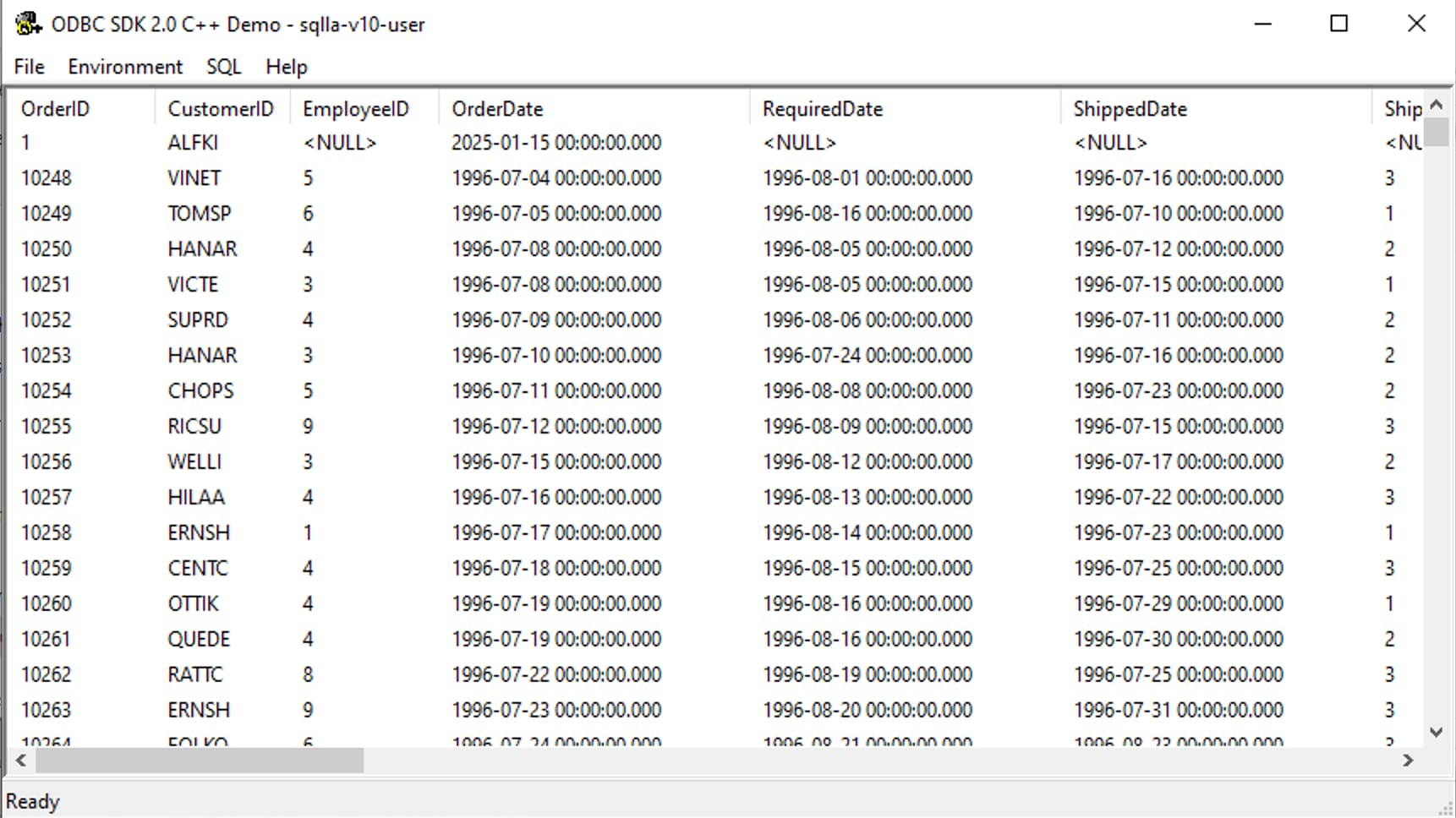
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues during the "Test Data Source" step or while connecting with applications, check the following common scenarios:
If the connection fails with a timeout error, ensure that:
- The SQL Server hostname or IP address is correct.
- Port 1433 (or your custom port) is open on the server's firewall.
- The SQL Server instance is actually running on the target machine.
If connecting to a specific instance (e.g., Server\InstanceName) fails:
- Ensure the SQL Server Browser service is running on the server. This service is required for resolving instance names to ports.
- Alternatively, specify the exact port number in the "Port" field instead of relying on the instance name resolution.
If you receive "Login failed for user...", verify:
- You are using the correct Authentication Method (Windows Integration vs. SQL Server Authentication).
- If using SQL Server Authentication, ensure "Mixed Mode Authentication" is enabled on the server.
Frequently Asked Questions
curl -O https://download3.openlinksw.com/uda/components/10.0/x86_64-generic-win-64/wal10mzzz.msi.
wal10mzzz.msi for the x86_64-generic-win-64 platform.
sql_lt.lic file during installation or check the
box to install the license file later.
\InstanceName to the
ServerName (e.g., ServerName\InstanceName) in the Host Name field.
az account get-access-token with the appropriate
resource URL to generate the AccessToken.